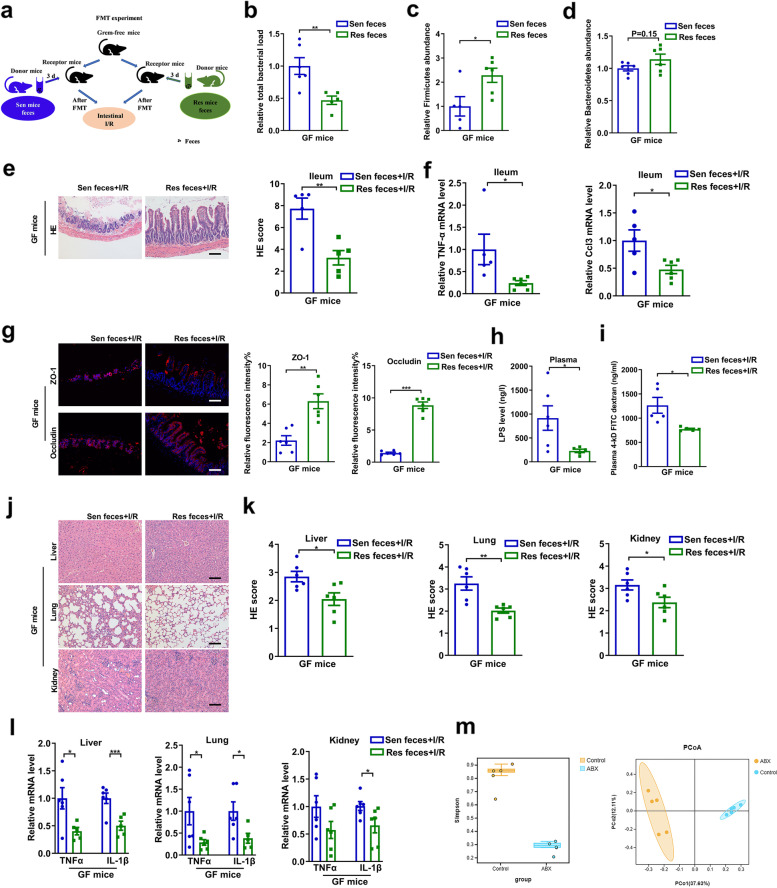
Fig. 2.
Gut microbiota from Res mice independently alleviates I/R-induced intestinal, liver, lung, and kidney tissue damage. a FMT experimental design. GF mice were subjected to intestinal ischemia for 60 min and reperfusion for 120 min after 3 days of transplantation. b–d The total bacterial load and the abundance of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in the feces 3 days after transplantation. e HE staining in the ileum. Scale bar = 100 μm. f The mRNA levels of proinflammatory factors in the ileum. g–h Tight junction mRNA levels and protein levels in the ileum and relative plasma endotoxin level. Scale bar = 100 μm. i FD-4 level in the plasma. j–k HE staining in the liver, lung, and kidney and pathology score. Scale bar = 100 μm. l The mRNA levels of proinflammatory factors in the liver, lung, and kidney. m Alpha diversity indices (Simpson) and PCoA analysis of Control and ABX-treated mice group. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM. n = 5–6. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 were determined using two-tailed Student’s t test. ABX, antibiotic; FD-4, FITC-dextran 4-KD; FMT, fecal microbiota transplantation; GF, germ-free; HE, hematoxylin-eosin; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion. PCoA, principal coordinates analysis