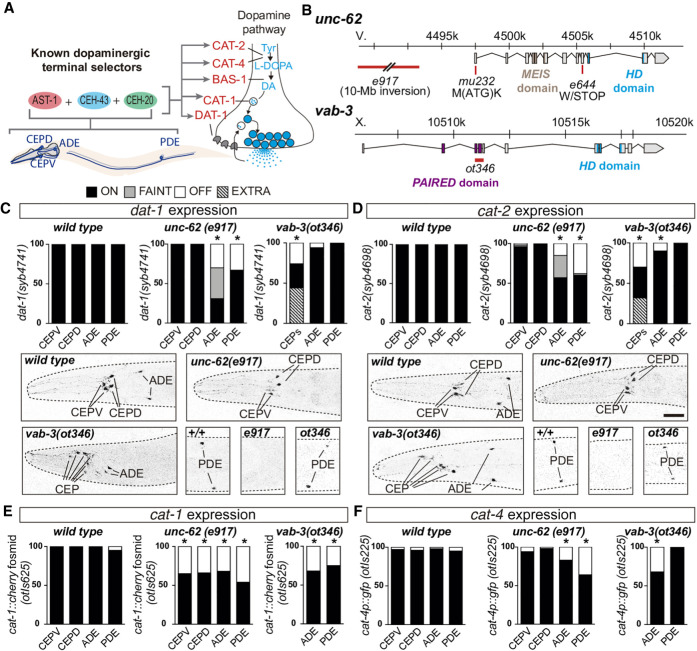
Figure 2.
unc-62/MEIS-HD and vab-3/PAIRED-HD are required for correct dopamine pathway gene expression in all dopaminergic subtypes. (A) AST-1/ETS, CEH-43/DLL HD, and CEH-20/PBX HD are known terminal selectors for all four dopaminergic neuron types and directly activate expression of genes coding for the dopamine pathway components. (CAT-1/VMAT1/2) vesicular monoamine transporter; (CAT-2/TH) tyrosine hydroxylase; (CAT-4/GCH1) GTP cyclohydrolase; (BAS-1/DDC) dopamine decarboxylase; (DAT-1/DAT) dopamine transporter; (DA) dopamine; (Tyr) tyrosine. (B) Schematic representation of unc-62 and vab-3 gene loci and alleles used in the analysis. (C,D) Endogenous dat-1 and cat-2 dopamine pathway gene reporter expression analysis in unc-62(e971) and vab-3(ot346) alleles. For cat-2 and dat-1 analysis, disorganization of vab-3(ot346) head neurons precluded us from distinguishing CEPV from CEPD and thus are scored as a unique CEP category. Reporter expression quantification and representative micrographs of each genotype are shown. n > 50 animals each condition; (*) P < 0.05 compared to wild type, Fisher's exact test. Scale: 25 µm. (E) cat-1(otIs625) fosmid recombineered reporter (integrated multicopy array) expression analysis in unc-62(e971) and vab-3(ot346) alleles. Disorganization of vab-3(ot346) head precluded the identification of CEPs among other mCherry expressing neurons in the region, and thus only ADE and PDE scoring is shown. n > 50 animals each condition; (*) P < 0.05 compared to wild type. (F) cat-4(otIs225) transcriptional reporter (integrated multicopy array) expression analysis in unc-62(e971) and vab-3(ot346) alleles. Disorganization of vab-3(ot346) head precluded the identification of CEPs among other GFP expressing neurons in the region, and thus only ADE and PDE scoring is shown. n > 50 animals each condition; (*) P < 0.05 compared to wild type.