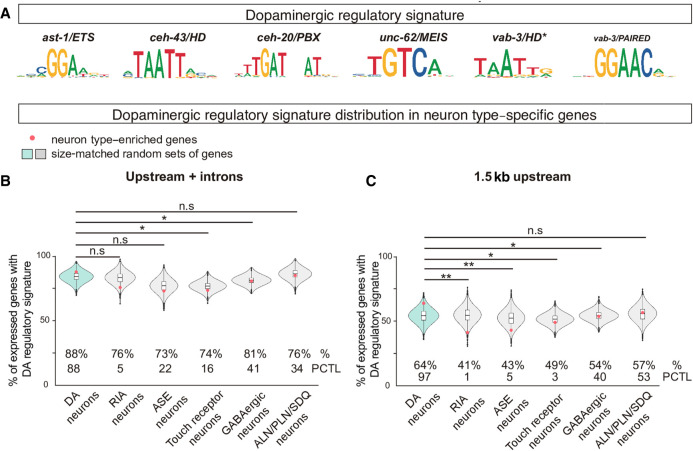
Figure 5.
The dopaminergic regulatory signature is preferentially associated with dopaminergic expressed genes. (A) Position weight matrix logos assigned to each member of the dopaminergic terminal selectors. The dopaminergic regulatory signature is defined by the presence of at least one match for each of the six PWM in <700-bp DNA window. (B) Dopaminergic regulatory signature is slightly more prevalent in the upstream and intronic sequences of the set of 86 genes with enriched expression in dopaminergic neurons (red dot in blue violin plot) compared to five additional gene sets with enriched expression in nondopaminergic neurons (RIA, ASE, Touch receptor neurons, GABAergic neurons, and ALN/PLN/SDQ). However, dopaminergic signature presence in dopaminergic-enriched genes is not higher than the mean of 10,000 sets of random comparable genes (red dot location inside the blue violin plot). (%) Percentage of genes with assigned dopaminergic regulatory signature; (PCTL) percentile of the real value (red dot) in the 10,000 random set value distribution. Brunner-Munzel test; (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01. (C) Dopaminergic regulatory signature in proximal regions (1.5 kb upstream ATG) is more highly enriched in dopaminergic expressed genes compared to other nondopaminergic expressed genes, and dopaminergic signature presence in dopaminergic-enriched genes is higher than the mean of 10,000 sets of random comparable genes (red dot location inside the blue violin plot), suggesting proximal regulation has a major role in dopaminergic terminal differentiation. See B for abbreviations and statistics.