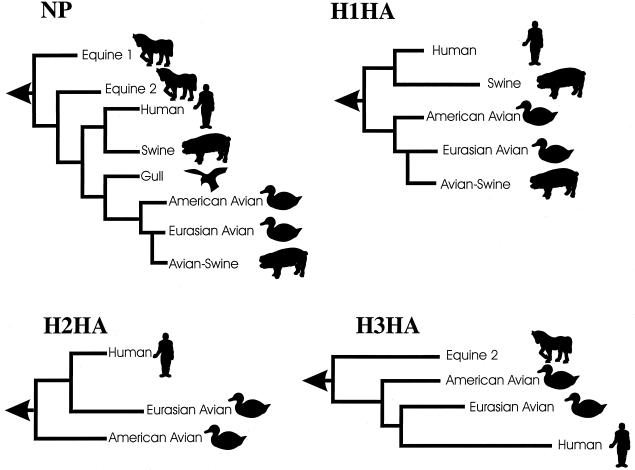
FIG. 3.
Phylogenetic relationships among influenza A virus genes. These generalized phylogenetic trees are derived from references 53 (NP, rooted to influenza virus NP), 80 (H1 HA, rooted to H2 HA), 164 (H2 HA, rooted to H5 HA), and 11 (H3 HA, rooted to H4 HA). Horizontal distances are proportional to the number of nucleotide differences needed to join the gene sequences, while vertical lines are used for spacing branches and labels. The arrow at the left of each tree represents the node connecting the influenza B virus homologue. Equine 1, H7N7 subtype (e.g., A/Equine/Prague/56); Equine 2, H3N8 subtype (e.g., A/Equine/Miami/63); Human NP, H1N1, H2N2 and H3N2 subtypes; Swine, classic swine viruses of the H1N1 subtype (e.g., A/Swine/Iowa/15/30); Gull, H13 gull viruses; Avian-Swine, European swine viruses derived from an avian virus.