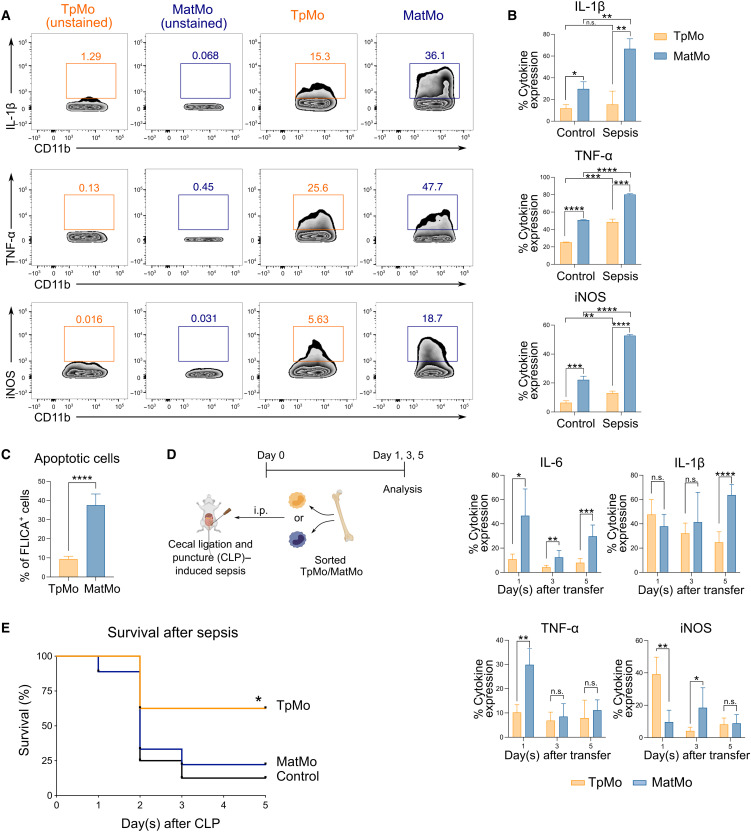
Fig. 7. TpMos display protective functions during sepsis by balancing the proinflammatory functions of MatMos.
(A) TpMos and MatMos were sorted and analyzed for the expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, and iNOS after stimulation with LPS. (B) Control and CLP-induced septic BM TpMos and MatMos were stimulated with LPS and analyzed for the expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, and iNOS. (C) LPS-stimulated control BM TpMos and MatMos were analyzed for apoptotic cells using FLICA Poly Caspase. (D) TpMos and MatMos were sorted from CD45.1 mice and adoptively transferred into CLP-induced CD45.2 recipient mice via the intraperitoneal route. Analysis of PL of recipient mice for transferred cells was performed on days 1, 3, and 5 after adoptive transfer for the expression of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and iNOS. Results are expressed as means ± SD (n = 4 to 6) and representative of one of three experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 (Student’s t test). (E) TpMos or MatMos were sorted and adoptively transferred into recipient mice shortly after they were subjected to CLP. The mortality of these recipient mice was assessed using the Kaplan-Meier survival curve. Results are representative of one of three independent experiments (n = 10). *P < 0.05 (Mantel-Cox).