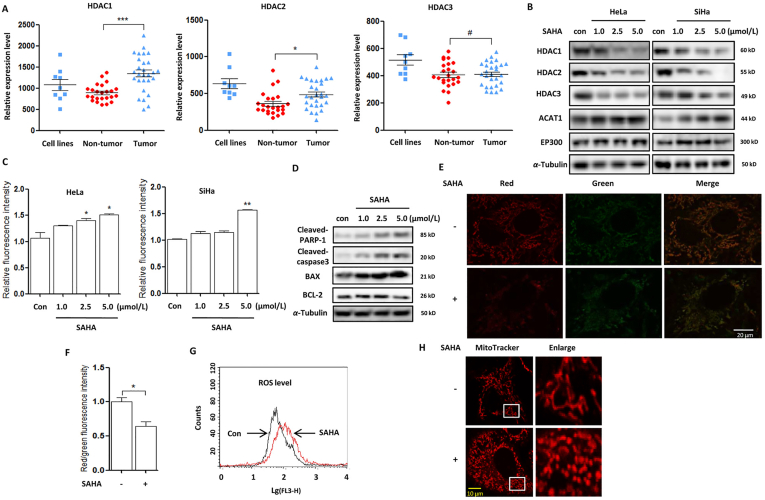
Figure 1.
SAHA treatment decreases HDACs expression and induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. (A) Analysis of the expression levels of HDAC1/2/3 in human cervical cancer cell lines, tumor & nontumor tissues from Oncomine database. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗P<0.001, #P>0.05. (B) HeLa and SiHA cells were treated with different doses of SAHA (1.0, 2.5, and 5.0 μmol/L) for 24 h as designated. Cells were harvested and lysed for Western blotting. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. (C) as in (B), cells were stained with the Annexin V, Pacific Blue™ conjugate and measured by BD FACS™. Cell fluorescence was calculated and statistically analysed. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. (D) Cell lysates were prepared from SAHA-treated SiHA cell and subjected to Western blotting analysis using antibodies against PARP-1 and caspase3. (E) and (F) SiHA cells were first treated with SAHA (5 μmol/L, 12 h) and then stained with 2 μmol/L JC-1 dye for 15 min at 37 °C. Fluorescence of J-aggregates (red) and J-monomers (green) was examined either by confocal microscope (scale bar = 10 μm) or BD FACS™. The ratio of J-aggregates to J-monomers was calculated as indicated and statistically analysed. ∗P < 0.05. (G) as in (F), mitochondrial ROS was detected by mitochondrial superoxide indicator (5 μmol/L, 30 min) and flow cytometry graph was shown. (H) as in (E), SAHA-treated cells were stained using MitoTracker™ Red CMXRos (100 nmol/L, 15 min) for mitochondrial length. Confocal Microscope was performed for evaluation. Scale bar = 10 μm.