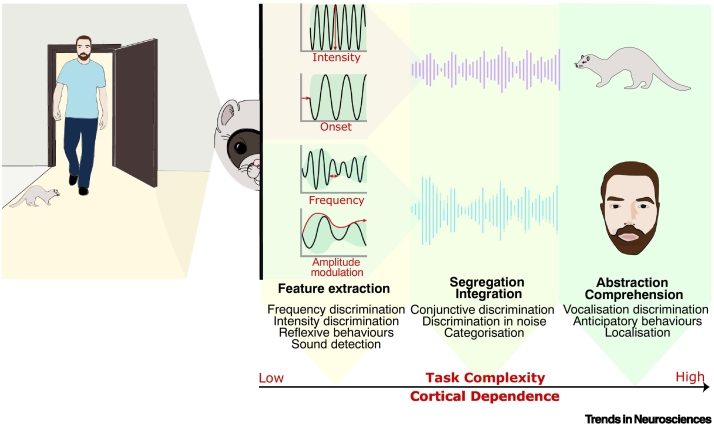
Figure 3.
Outline of processing stages involved in auditory scene analysis and associated auditory behaviours.
Natural scenes (on the left) consist of a variety of sound sources producing sounds simultaneously. After sounds arrive at the ear, individual acoustic features are extracted, largely at the subcortical level. Accordingly, tasks probing auditory feature extraction are only mildly affected by AC inactivation. The extracted features are then segregated into separate sound sources and integrated into objects defined by conjunctive features. Finally, sounds are interpreted and acted upon, based on their behavioural relevance. The inactivation studies reviewed in the main text support the idea that as task complexity increases through these processing stages, auditory cortex plays an increasingly critical role in successful performance.