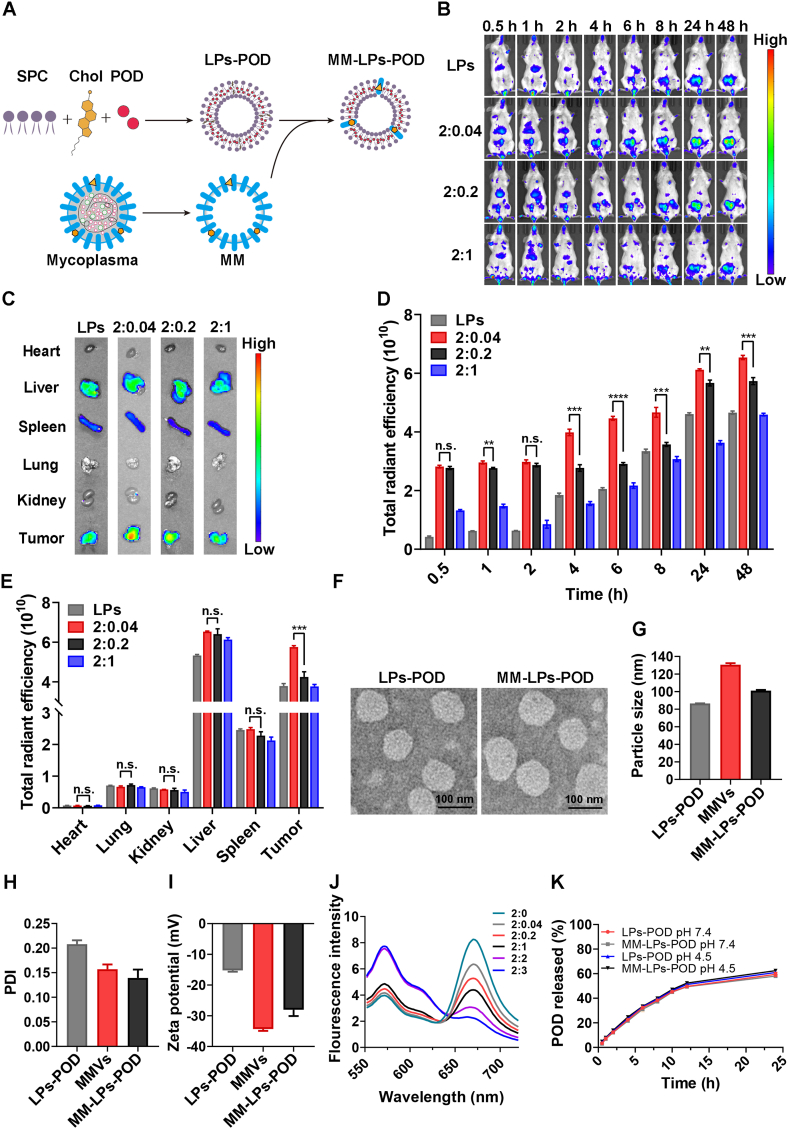
Figure 1.
Fabrication and in vitro characterization of MM-LPs-POD. (A) Schematic illustration of the preparation of MM-LPs-POD (B–E) Optimization of the mass ratio of LPs to MM protein was studied by IVIS. (B) Representative living images and (C) ex vivo fluorescence imaging of tumors and main organs excised from mice at 48 h after injection. (D) Corresponding quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity at the tumor sites (n=3). (E) Corresponding quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity of major organs (n=3). (F) TEM imaging (G) size, (H) PDI, and (I) zeta potential of LPs-POD and MM-LPs-POD (n=3). (J) LPs stained with FRET pair-dyes DiD and DiI were fused with increasing ratios of MM and fluorescence spectrum was recorded. The ratio represents the mass ratio of LPs to MM protein (K) In vitro cumulative drug release of LPs-POD and MM-LPs-POD in PBS at pH values of 7.4 and 4.5. Data are shown as the mean±SD and analyzed by unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. ∗P<0.05, ∗∗P<0.01, ∗∗∗P<0.001. n.s., not significant.