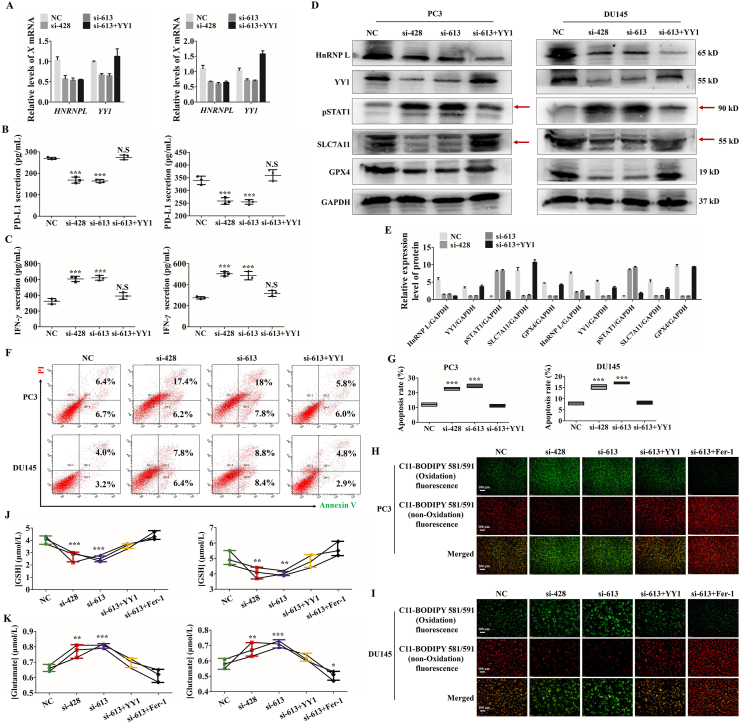
Figure 7.
HnRNP L inhibits Jurkat T cells-mediated ferroptosis of CRPC cells via the YY1/PD-L1 axis. (A) The qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of HnRNP L and YY1 in stable CRPC cells (PC3 and DU145) with or without HnRNP L inhibition and YY1 overexpression. (B) PD-L1 in cell culture medium from the stable CRPC cells (PC3 and DU145) with or without HnRNP L inhibition and YY1 overexpression was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (C) IFN-γ in cell culture medium from the activated Jurkat T cells after co-cultured with the stable CRPC cells (PC3 and DU145) with or without HnRNP L inhibition and YY1 overexpression was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (D) and (E) Western blotting analysis of the expression of HnRNP L, YY1, pSTAT1, SLC7A11 and GPX4 after co-culture with the activated Jurkat T cells in transfected CRPC cells (si-HnRNP L or/and YY1 overexpression). GAPDH was used as a loading control. Red arrow indicates the main bands for analysis. (F) and (G) Representative images of annexin-V/propidium iodide staining showing increased apoptosis in CRPC cells treated with si-HnRNP L and decreased apoptosis in CRPC cells treated with both si-HnRNP L and YY1 overexpression after co-culture with the activated Jurkat T cells (F). Statistical results were represented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments (G). (H) and (I) The changes of lipid ROS accumulation in transfected PC3 and DU145 (si-HnRNP L or/and YY1 overexpression or/and ferrostatin-1) cells after co-culture with the activated Jurkat T cells were measured by fluorescence microscope. (J) and (K) The stable CRPC cells (PC3 and DU145) with or without HnRNP L inhibition and YY1 overexpression or ferrostatin-1 were co-cultured with the activated Jurkat T cells for 48 h, and the amount of glutamate released into culture medium was measured. Indicated cells co-cultured with the activated Jurkat T cells for 48 h were lysed, and the intracellular GSH level was measured. The data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). The data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and post-hoc assays and student’ s t-test. ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001, vs. NC control.