Figure 4 –
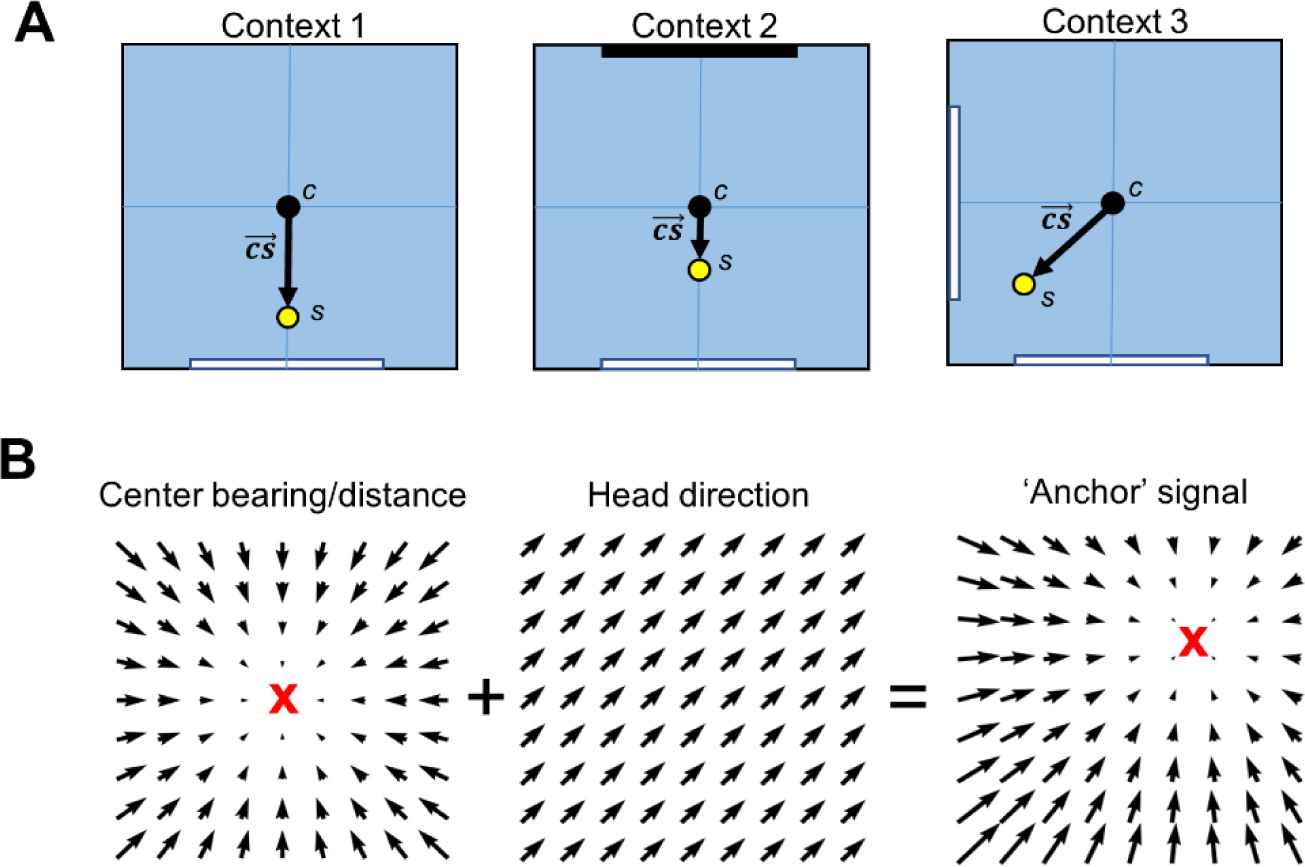
Potential interactions between egocentric and HD signals in representing spatial context. A) Top-down schematic views of a recording arena with identical geometries but different visual landmarks, along with the locations of the unweighted centroid c based on all physical cues of the environment and the salience centroid s which is weighted by the salience of each physical cue. Note that s is displaced preferentially toward the location of a white cue card in each context, and to a lesser extent toward the black cue card in context 2. The salience vector connects the unweighted centroid to the salience centroid and is unique for each context. B) Left, vector field showing the firing preferences of a center-bearing by center-distance cell; middle, vector field showing the firing preferences of an HD cell with PFD pointing northeast; right, resultant vector field after summing the center-bearing/distance and HD fields. Note that the focal point of the center-bearing/distance field (anchor point; indicated by a red X) has shifted toward the northeast after summing with an HD signal.
