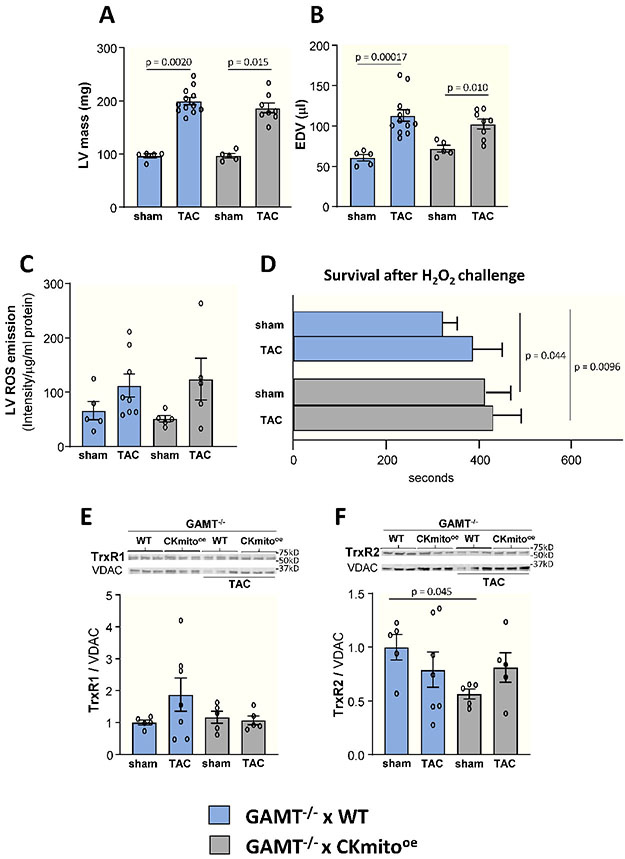
Figure 5. Cardiac-specific overexpression of mitochondrial creatine kinase (CKmito) does not attenuate pathologic remodeling and ROS burden in creatine-deficient mice.
Creatine-deficient guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase (GAMT) knock-out mice were crossed with cardiac-specific CKmito overexpressing (GAMT−/− x CKmitooe) or WT (GAMT−/− x WT) mice. Cardiac (A) left ventricular (LV) mass and (B) end-diastolic volume (EDV) for GAMT−/− x CKmitooe and GAMT−/− x WT mice with or without TAC were determined by in vivo MRI (experimental replicates: n=5 (GAMT−/− x WT sham or GAMT−/− x CKmitooe sham), n=12 (GAMT−/− x WT TAC), and n=8 (GAMT−/− x CKmitooe TAC) (A-B). (C) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production measured by EPR spectroscopy in LVs of GAMT−/− x CKmitooe and GAMT−/− x WT sham or TAC hearts (experimental replicates: n=5 (GAMT−/− x WT sham, GAMT−/− x CKmitooe sham, GAMT−/− x CKmitooe TAC) and n=8 (GAMT−/− x WT TAC). (D) Cardiomyocytes were isolated from GAMT−/− x CKmitooe, and GAMT−/− x WT sham or TAC hearts were exposed to H2O2 (50 μM) for 700 s and time to irreversible arrhythmia/cell death was monitored (experimental replicates: n=19 cells isolated from 3 mice (GAMT−/− x WT sham), n=12 cells isolated from 2 mice (GAMT−/− x WT TAC or GAMT−/− x CKmitooe TAC), and n=18 cells isolated from 3 mice (GAMT−/− x CKmitooe sham)). Representative immunoblots and summary of data showing LV expression levels of (E) TrxR1 (thioredoxin reductase 1) and (F) TrxR2 (thioredoxin reductase 2) normalized to VDAC (voltage-dependent anion channel) and presented as relative to the amount of protein detected in sham GAMT−/− x WT hearts (experimental replicates: n=5 (GAMT−/− x WT sham, GAMT−/− x CKmitooe sham, GAMT−/− x CKmitooe TAC) and n=7 (GAMT−/− x WT TAC) (E-F)). Graphs show data points for individual mice (A-C, E-F). Data were tested for normality using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality and analyzed by Wilcoxon signed rank test followed by pair-wise, two-sided multiple comparison analysis (Dwass, Steel, Crichlow-Fligner Method) (A), two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc multiple comparison test (B-C,E-F), or a generalized estimating equation model was used to take into account the correlation of within-subject data. (D). The error bars represent ±SEM.