Figure 6: EBF1, but not TCF1 or LEF1 alone, maintains chromatin opening.
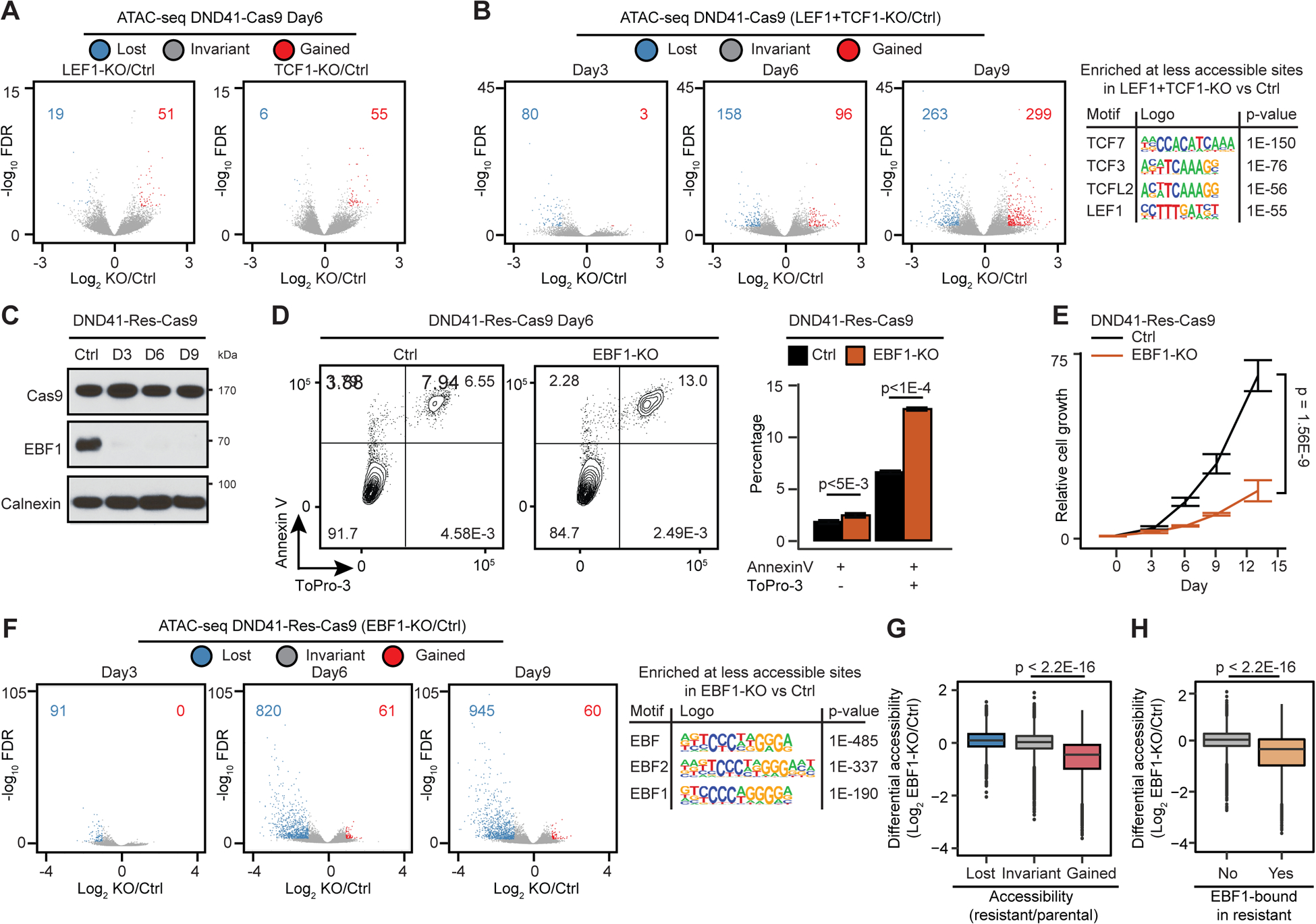
(A, B) Differential opening post deletion of LEF1 or TCF1 (A), or both (B) in Cas9-expressing DND41 (DND41-Cas9) at the noted dates. (B, left): the most enriched motifs.
(C) EBF1 levels post its deletion in Cas9-expressing resistant DND41 (DND41-Res-Cas9). D: day; control: Calnexin.
(D, E) Effect of EBF1 loss on apoptosis, death (D) and relative growth (E) in DND41-Res-Cas9 cells. 3 biological with mean ± SD of 5 technical replicates (t-test).
(F) Differential opening and enriched motifs post EBF1 deletion in DND41-Res-Cas9.
(G, H) Differential ATAC-seq post EBF1 deletion in DND41-Res-Cas9 per differential opening (G) or EBF1 binding (H) during resistance development (Wilcoxon test).
