Figure 5:
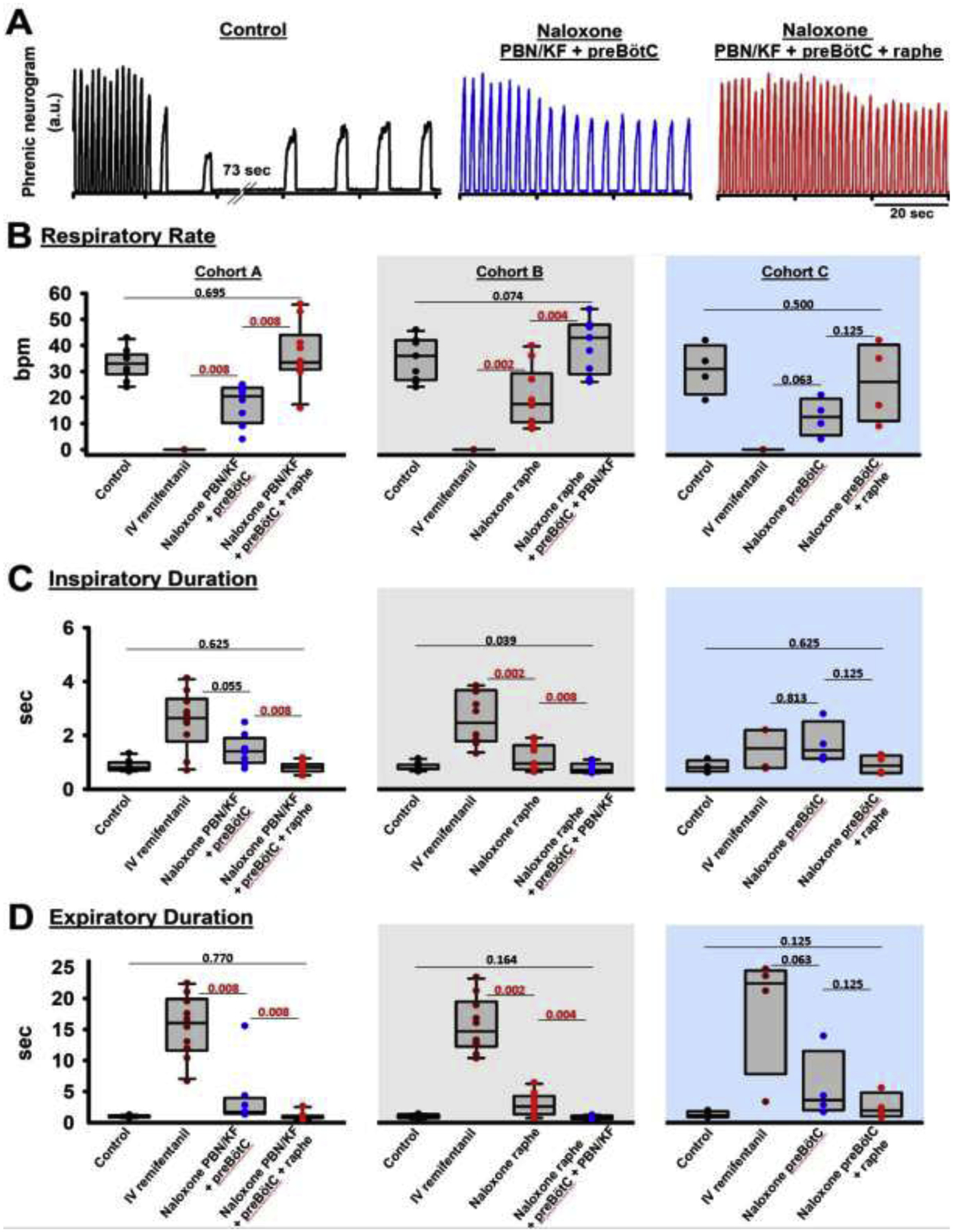
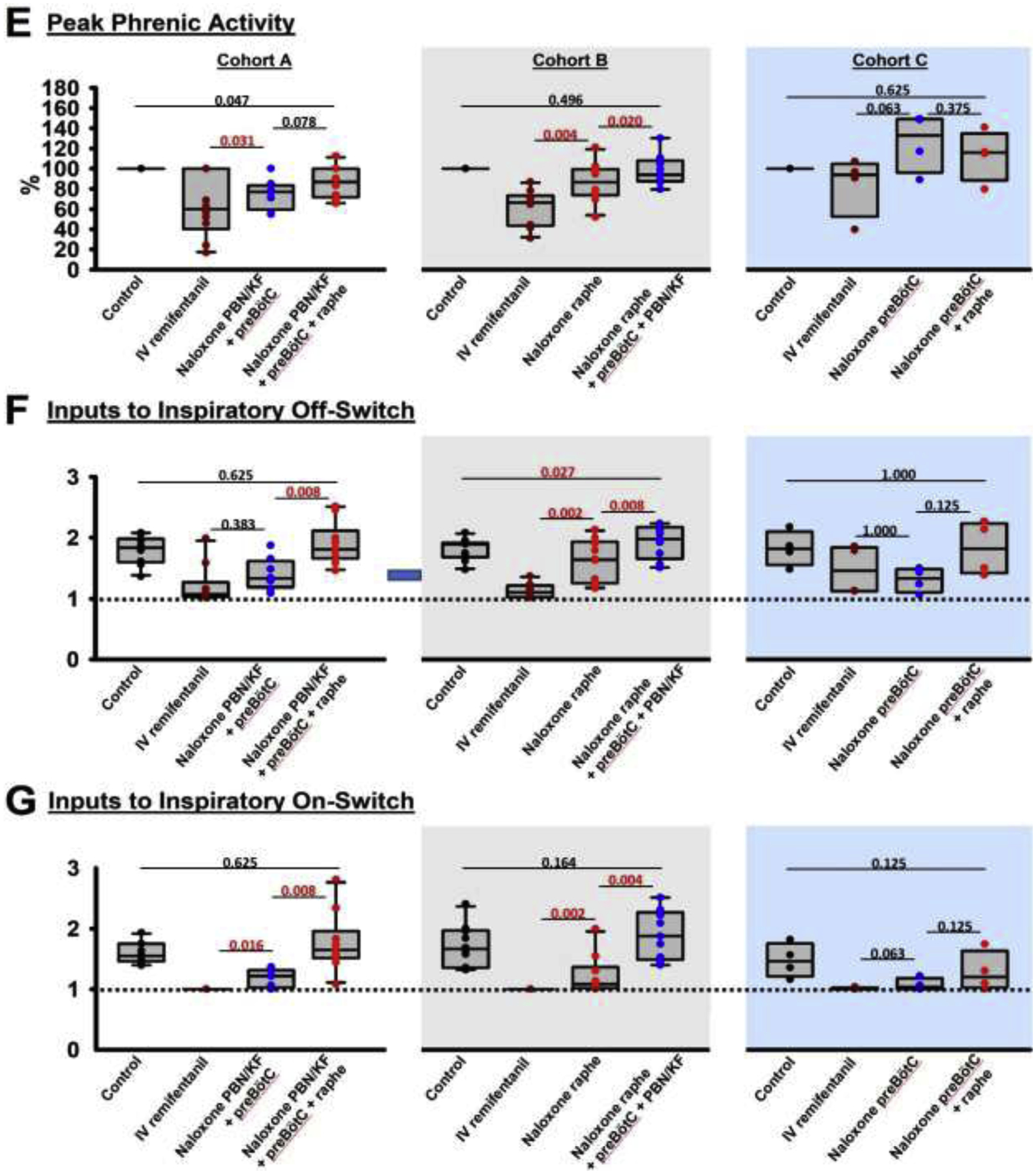
“Apneic” remifentanil concentrations. Bilateral naloxone injection into the Parabrachial Nucleus/Kölliker-Fuse Complex (PBN/KF), the preBötzinger Complex including the premotor neurons (preBötC), and the Caudal Medullary Raphe (raphe) completely prevented the respiratory rate depression from an intravenous remifentanil bolus that caused apnea >60sec under control conditions. A: Phrenic neurogram tracings from the same rabbit shown in figure 4 shows that sequential naloxone injections increasingly reduced respiratory rate depression from the “apneic” bolus. (B-E) Pooled data for measured respiratory parameters and (F,G) values for the inputs to inspiratory off-switch and on-switch, derived from inspiratory and expiratory duration. Data are presented separately for Cohort A (left panels in white, n=10), Cohort B (center panels in grey, n=10), and Cohort C (right panels in blue, n=4). Bars indicate that the difference between values from two subsequent injections or control was tested against no change (Wilcoxon signed rank test). The levels of significance below the critical P=0.0167 are highlighted in red. The dotted line indicates the threshold value, set at 1 in our model, which the sum of inputs must exceed to result in phase switch (see Appendix 1 in (1)).
