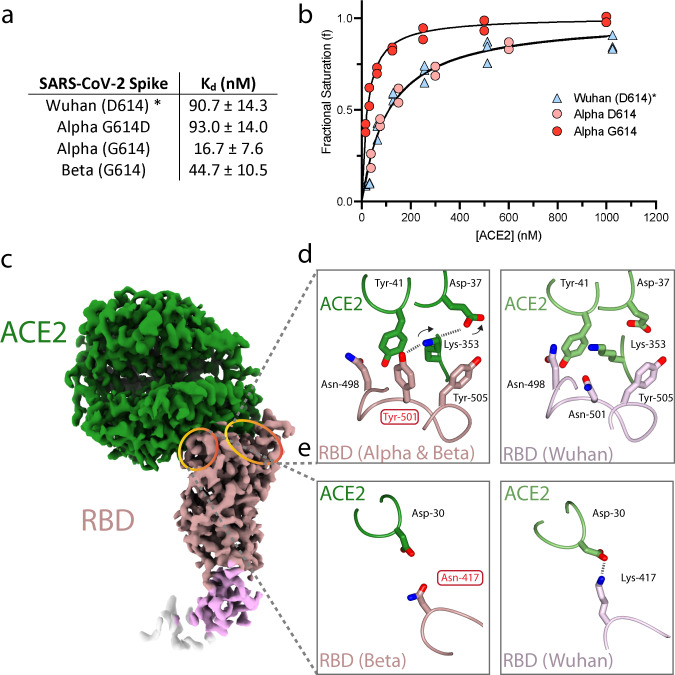
Fig. 2. Variant spike binding to receptor ACE2.
a Kd of variant spikes binding to ACE2 measured using biolayer interferometry and calculated from koff/kon analysis (see Supplementary Fig. 7 for details). b Plots of fractional saturation binding measurements with data for the Alpha variant shown in red, Alpha variant with G614D substitution in pink, and Wuhan (D614) spike in blue. Wuhan (*the data for which shown here are adapted from our previous work47) and Alpha D614 spike show almost identical affinity towards ACE2. Similar results were obtained for G614 vs D614 mink (Y453F) spike (Supplementary Figs. 4 and 7). c cryoEM density of the complex of Beta variant S1 with ACE2, with ACE2 coloured in green, RBD in rosy brown, RBD subdomain in plum, with the remaining S1 disseminated density in cream. d, e Detail of changes in the binding interfaces present in variants (left column) compared to the Wuhan strain (right column). d The N501Y substitution present in both the Beta and Alpha variants allows formation of a new hydrogen bond or a salt bridge. e The K417N substitution present in the Beta variant eliminates a salt bridge between the RBD and ACE2. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.