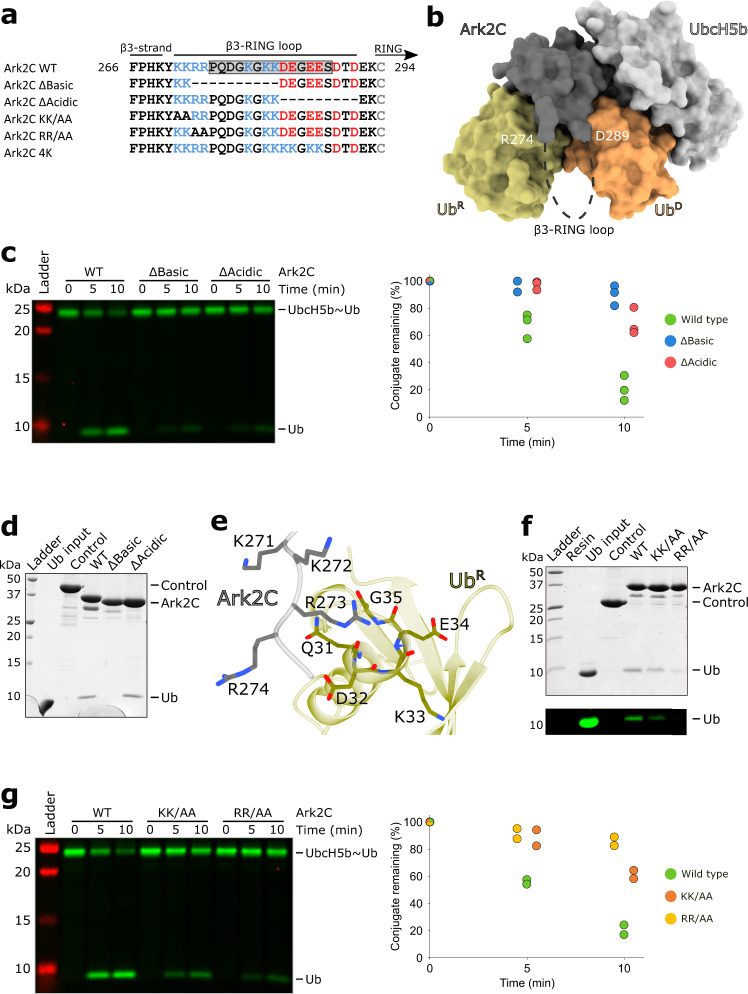
Fig. 4. Analysis of the β3-RING loop and its involvement in coordinating UbR.
a Sequences of the β3-RING loop constructs and mutants used in this study. Residues in the grey box in the WT sequence were missing from the crystal structure. b Surface diagram of the activated complex with the missing residues in the β3-RING loop shown as a dashed line (black) and the position of the last modelled residues in the crystal structure indicated. c Discharge assays assessing the ability of the indicated Ark2C deletion mutant proteins to promote hydrolysis of the UbcH5b~Ub conjugate. Ubiquitin used to prepare the UbcH5b~Ub conjugate was labelled and the gel was imaged as described in Fig. 1. The assay was performed in triplicate and the quantified data is shown to the right. d GST-pulldown assay comparing the ability of the Ark2C-ΔBasic and -ΔAcidic deletion constructs to bind ubiquitin. e Close-up view of the contacts between the basic residues at the N-terminus of the β3-RING loop and UbR in the UbArk2C structure. f GST-pulldown assay to assess the contribution of basic residues to ubiquitin binding. g Discharge assay as in panel (c) evaluating the ability of the mutant proteins to promote ubiquitin release. The assay was done twice and the discharge of conjugate was quantified. Both c and g were performed using 0.25 μM E3 ligase and 5 mM l-lysine. Source data are provided in the Source Data file.