Figure 3.
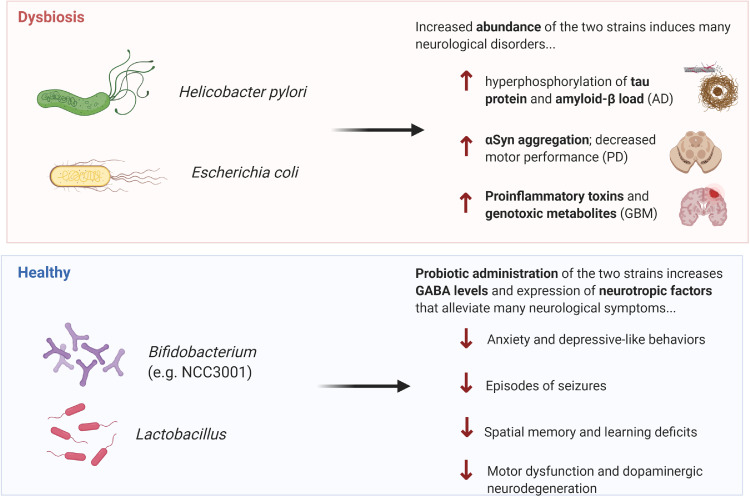
Microbials modulate the development and treatment of CNS disorders.
Microorganisms can promote production of essential metabolites, neurotransmitters, and other neuroactive compounds that influence the progression or treatment of various CNS diseases. In the setting of dysbiosis, increased prevalence of Helicobacter pylori and Escherichia coli, for example, was shown to induce the progression of many neurological disorders and symptoms including the hyperphosphorylation of tau protein and amyloid-Beta load (indicative of Alzheimer's disease), α-Synuclein aggregation and decrease motor performance (indicative of Parkinson's disease), and increased proinflammatory toxins and genotoxic metabolites (indicative of CNS malignancies). Conversely, probiotic administration of beneficial strains such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, for example, have been shown to alleviate many neurological symptoms through increase GABA levels and expression of neurotrophic factors. Effects include decreased anxiety and depressive-like behaviors, decrease episodes of seizures, decreased spatial memory & learning deficits, and decrease motor dysfunction & dopaminergic neurodegeneration.