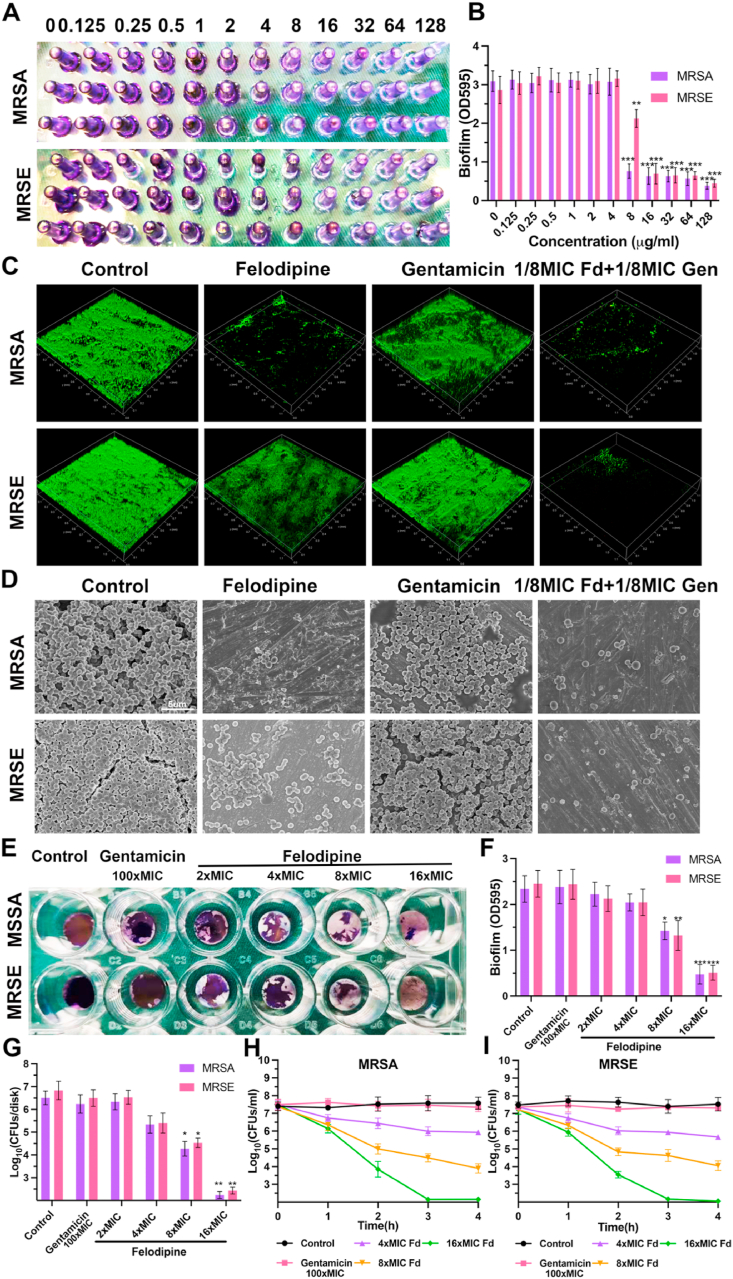
Fig. 5.
Felodipine combined with gentamicin against biofilm. (A) Minimum biofilm inhibitory concentration (MBIC) testing of felodipine against MRSA and MRSE. Biofilms was stained with crystal violet. (B) Biofilm mass was quantified by measuring sample absorbance at 595 nm using a spectrophotometer. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD; n = 3; ***p < 0.001. (C) After treated with felodipine or gentamicin, the biofilm formation on the surface of medical implant (Ti6Al4V disks) was stained with a bacterial viability kit and detected by CLSM. (D) SEM was conducted to observe the effect of felodipine or gentamicin in preventing biofilm formation. (E) Crystal violet staining was applied to examine the antibacterial efficacy of felodipine against established biofilms on the surface of implants. (F) Biofilms were quantified by measuring the absorbance of the samples at 595 nm using spectrophotometer. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD; n = 3; ***p < 0.001. (G) After treatment with different concentration of felodipine or gentamicin, the number of bacteria within the established biofilm was enumerated by the spreading plate method. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD; n = 3; ***p < 0.001. (H) After treatment with different concentration of felodipine or gentamicin, the number of MRSA persisters was counted at indicated time. (I) After treatment with felodipine or gentamicin, the number of MRSE persisters was counted at indicated time.