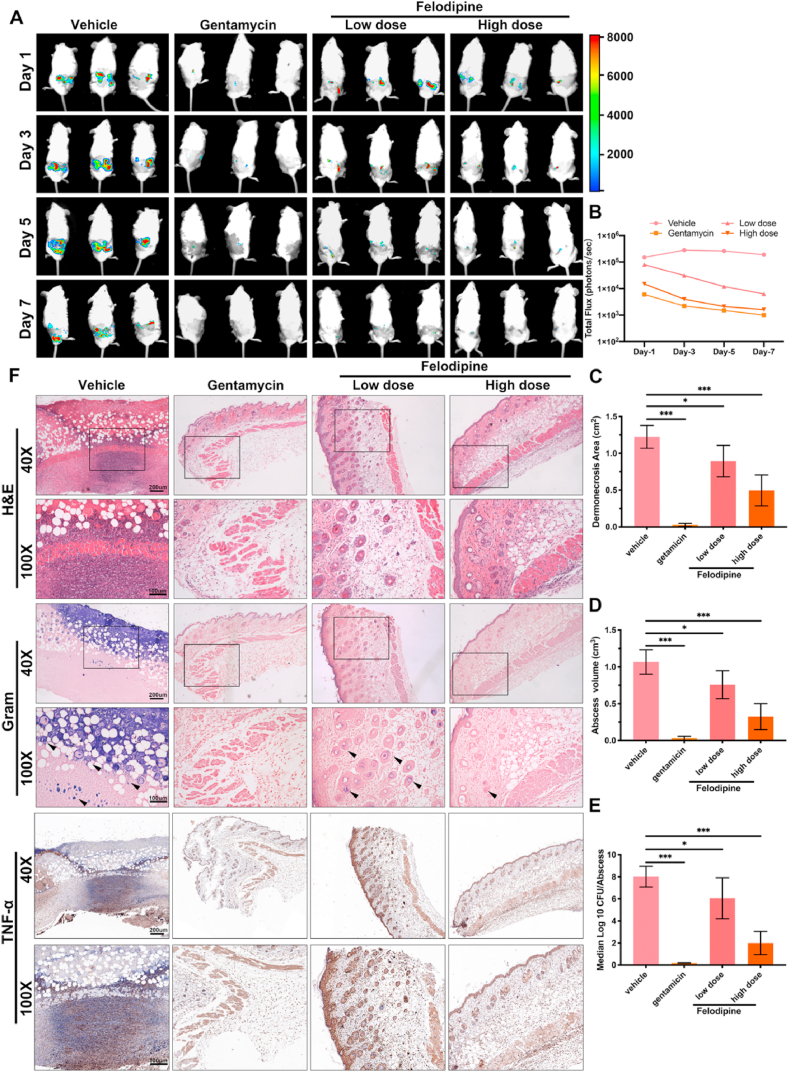
Fig. 7.
Felodipine reduces murine skin and soft tissue infections caused by bioluminescent Staphylococcus aureus Xen29. (A) Bioluminescence images were observed using an in vivo imaging system after treated with low dose of felodipine (20 mg/kg, s.c.), high dose of felodipine (40 mg/kg, s.c.) or gentamicin (80 mg/kg, s.c.). (B) Luminescence signals from regions of interest of each infection sites were quantified with the IVIS Living Image software. (C) After 7 days of treatment, the dermonecrosis areas were measured. Data are expressed as mean ± SD; n = 10; *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001. (D) After 7 days of treatment, the abscess volume was measured. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD; n = 10; *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001. (E) After 7 days of treatment, the number of bacteria within the abscesses was quantified. Data are expressed as the means ± SD; n = 10; ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001. (F) After 7 days of treatment, histological staining of infected tissues was conducted to evaluate the inflammatory response and bacterial loads. S. aureus was stained purple in Gram-stained tissues.