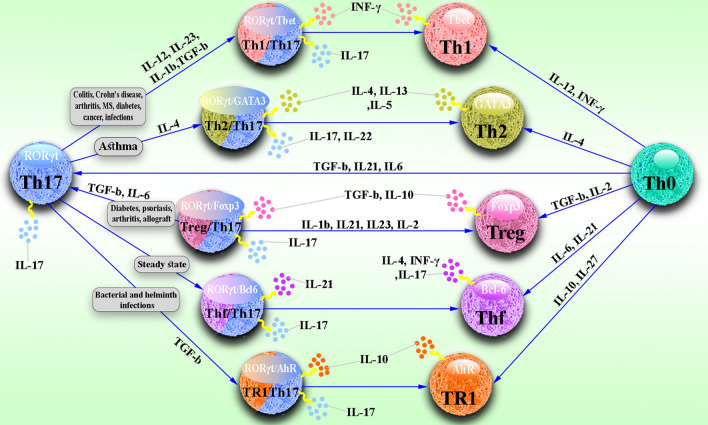
Fig. 1.
Plasticity of Th17. Th17 cells can mainly transform into TFH, Th2, TR1, Treg, and Th1 cells and exhibit a variety of contrasting functions depending on environmental conditions. During infections and autoimmune diseases, Th17 cells can acquire immune inhibitory functions by becoming TR1 or Treg cells. Th17 cells also change to TFH cells at a steady-state and participate in promoting IgA-producing B cells. Also, Th17 cells acquire pathogenic activity by changing to Th2 cells during asthma or Th1 cells during infection, cancer, and autoimmune diseases