Table 3.
Estimated Effects of Depression on Stroke Risk Under an Accumulation Model (Expressed on the Log Odds Scale) Comparing Conventional Regression and Inverse Probability Weighting to Estimate Marginal Structural Model Parameters in the Presence of a Late Study Start and Time-Varying Confoundersa
| Estimated Effect (Log RR) of Depression on Stroke Risk | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression in Midlife | Depression in Late Life | Lifetime Effect of Depression | |||||
| Analytical Method |
Log RR (
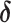 2)
2)
|
% Bias b |
Log RR (
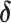 3)
3)
|
% Bias b |
Method of
Calculation |
Log RR | % Bias b |
| True effects | 0.69 | 0.69 |
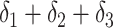
|
2.07 | |||
| Conventional regression | 0.56 | −19 | 0.69 | 0 |
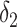 +
+ 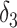
|
1.25 | −40 |
| IPW estimation of MSM | 0.74 | 7 | 0.69 | 0 |
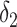 +
+ 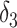
|
1.43 | −31 |
Abbreviations: AUD, alcohol use disorder; IPW, inverse probability weighting; MSM, marginal structural model; RR, risk ratio.
a Data were generated to mimic the effect of depression on stroke under the accumulation model: The true direct effect of depression at each time point doubled the odds of stroke, and depression increased the odds of depression at the subsequent time point by 50%. We assumed that depression approximately tripled the odds of AUD, that AUD increased the odds of depression at the subsequent time point by 50%, and that AUD doubled the odds of stroke. Data were generated with 10,000 replications and 100,000 people in each sample.
b Percent bias = [(average of 10,000 estimated effect − true effect of 0.69)/true effect of 0.69] × 100.
