Figure 3. Multivariate hazard ratios of cardiovascular disease according to joint categories of lifestyle and genetically determined sleep pattern.
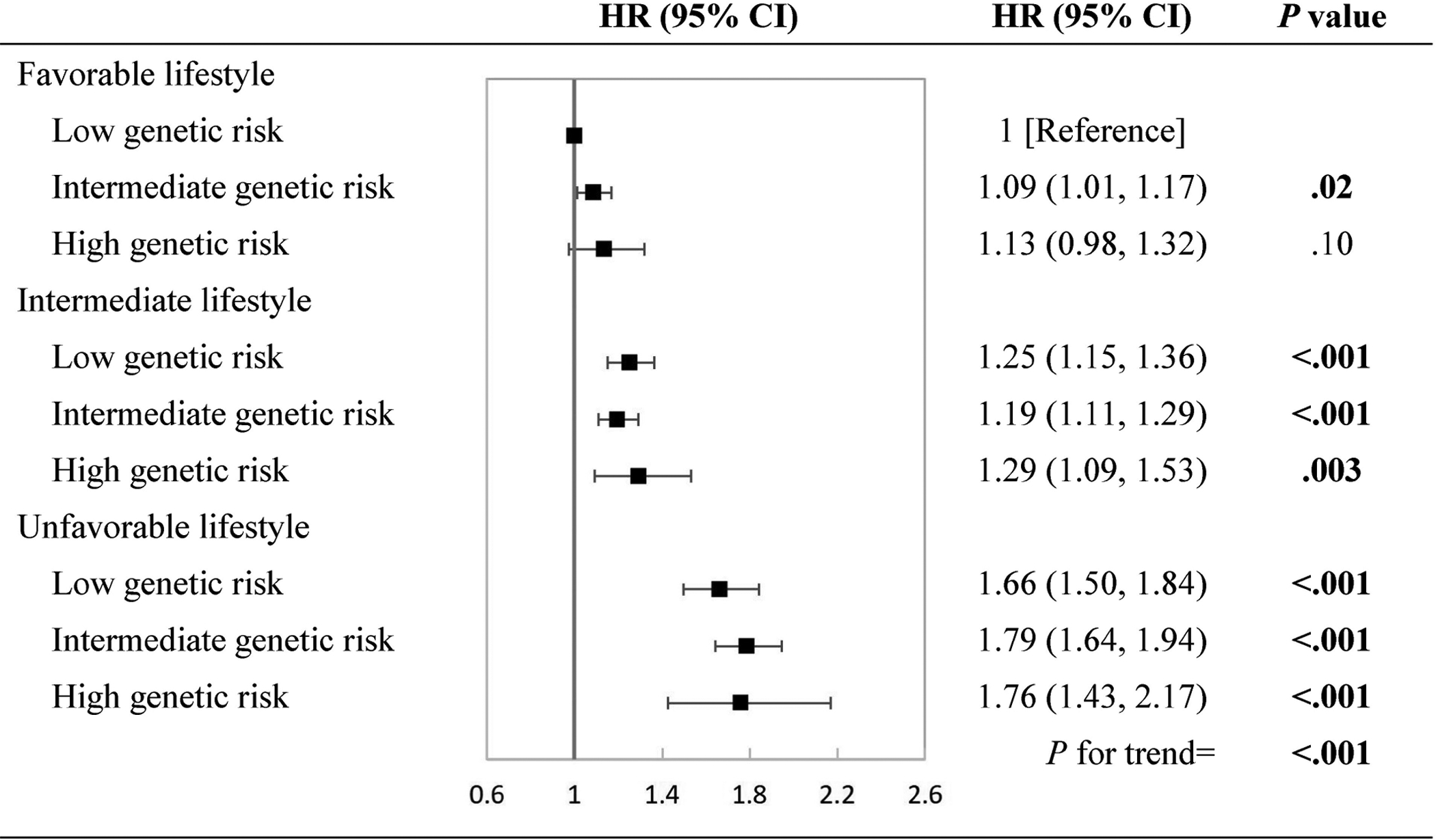
Low, intermediate, and high genetic risk indicated healthy, intermediate, and poor sleep pattern, respectively. Multivariate adjusted hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals of cardiovascular disease were estimated from Cox proportional hazards models, adjusted for sex, age, assessment center, batch effects (106 batches), the first 10 genetic principal components, Townsend deprivation index, income, family history of CVDs, medical history of cancer, diabetes, hypertension, angina, symptom of depression/anxiety, high cholesterol, insulin treatment, antihypertensive drugs, lipid treatment, aspirin use, hypnotics/antidepressants/anti-anxiety drugs, and body mass index. CI, confidence interval; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HR, hazard ratio.
