Figure 5. Chk1 plays a critical role in regulating STAT3 signaling.
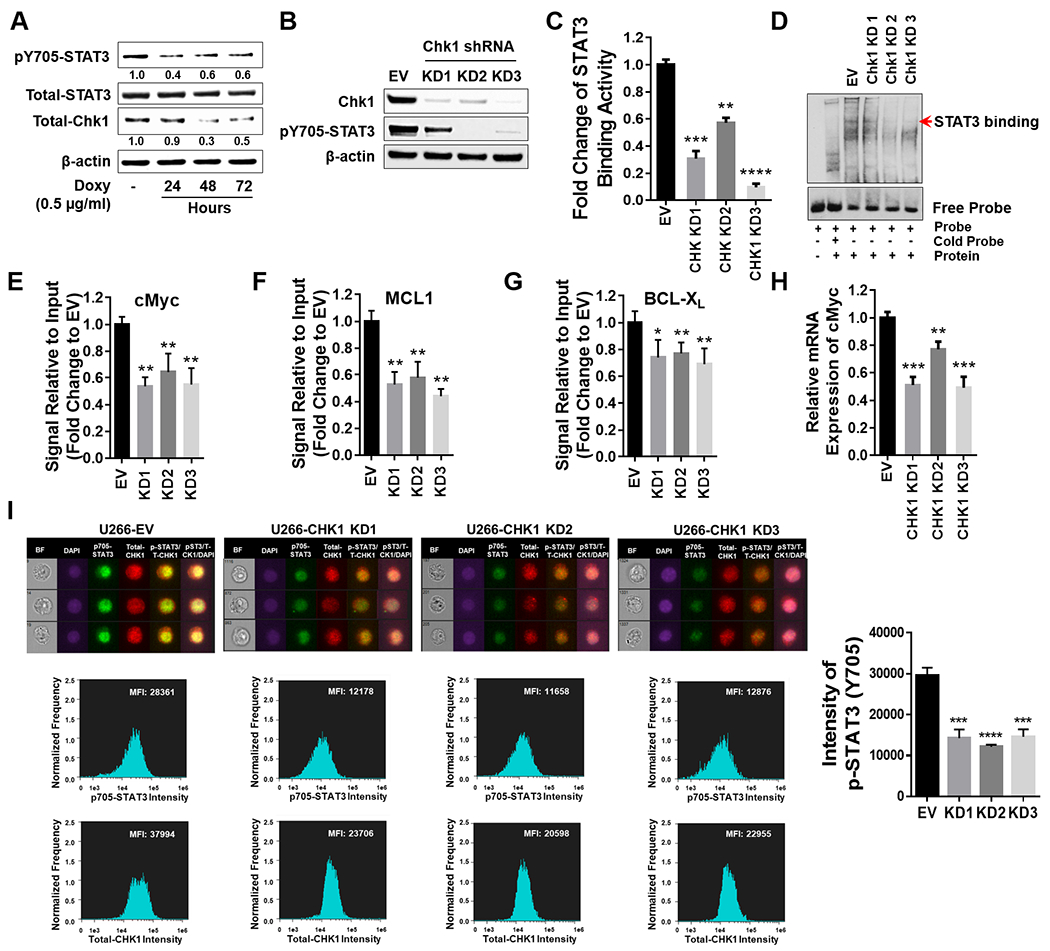
A, U266 cells were transfected with a Tet-on inducible Chk1 shRNA. Doxycycline (0.5 μg/ml) induced cells were collected at 24, 48 and 72 hr. Total lysates were immunoblotted for p-Y705 STAT3, total STAT3, and Chk1. β-actin was used as a loading control. Images were quantified and analyzed using ImageJ software. Data was normalized by the ratio of indicated protein/β-actin vs control. B-I, U266 cells were transfected with a lentivirus harboring Chk1 shRNA. B, Western blot analyses of Chk1 and p-Y705 STAT3 were performed. β-actin controls were assayed to ensure equivalent loading and transfer. C, The STAT3 DNA-binding ELISA was used to evaluate the ability of STAT3 in cellular nuclear extracts to bind to its corresponding consensus sequence immobilized on a 96-well plate. D, EMSA assay of DNA-binding activity of STAT3 in Chk1 knock-down cells. E-G, ChIP experiments were performed to detect the presence of STAT3 at the promotor regions of BCL-XL, MCL-1, and c-Myc in Chk1 knockdown cells. Data was normalized with non-immune IgG (negative control) and STAT3 antibody, and relative fold change (vs UT) is presented. H, Relative mRNA expression of c-Myc was determined by real-time reverse transcription-PCR analysis. GAPDH served as an internal control. Relative fold change (vs EV) is presented. I, Cells were stained with p-Y705 STAT3, Chk1 and DAPI, and then visualized by fluorescence microscope and by ImageStream and representative cells are shown (BF = brightfield). Histograms of p-Y705 STAT3 intensity and fold change are shown. Representative data for at least three replicates. *, P < 0.05; ** = P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; **** = P < 0.0001.
