Figure 6.
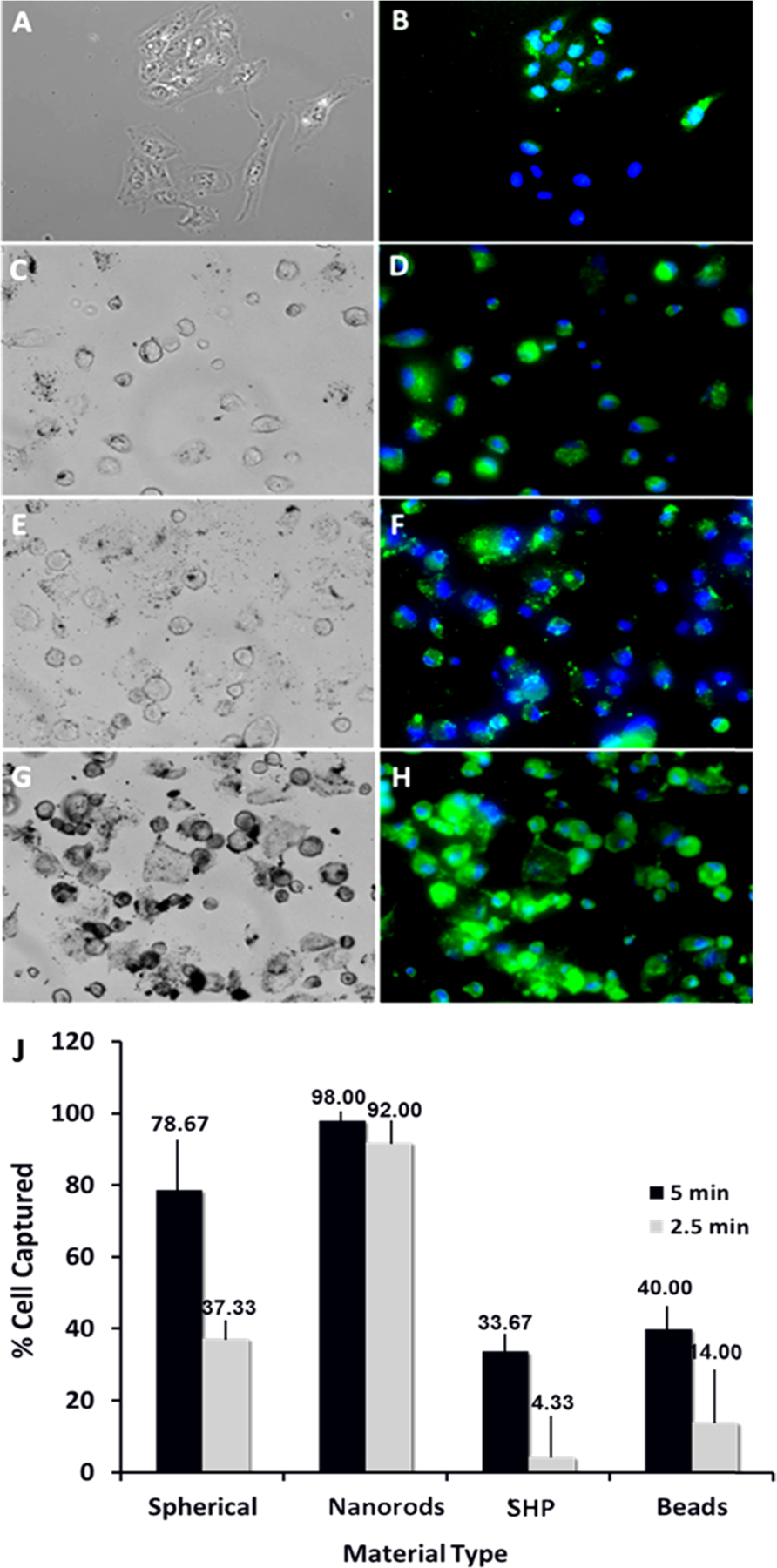
Magnetic separation of medulloblastoma cancer cells using different magnetic materials. Bright light (left panel) and corresponding florescent (right) microscopy images of the captured D556 cells using: beads (commercially available Dynobeads) (A, B), SHP (commercially available IONPs) (C, D), 50 nm IONPs (E, F), 50 nm IONRs (G, H), and cell capture performance (% cell captured) of different separation reagents (I). Cell separation experiment: step 1: cells were seeded with 0.2 mg/mL IONPs for 1 h at 4 °C; step 2: cells were detached, placed in Eppendorf tubes, and diluted to 1 mL of media; step 3: cells were exposed to magnetic separation for 2.5 min and then for 5 min; step 4: the suspension containing the nontargeted cells were removed; step 5: IONPs was captured, and the separated cells were diluted in media, counted, and prepared for microscopy study.
