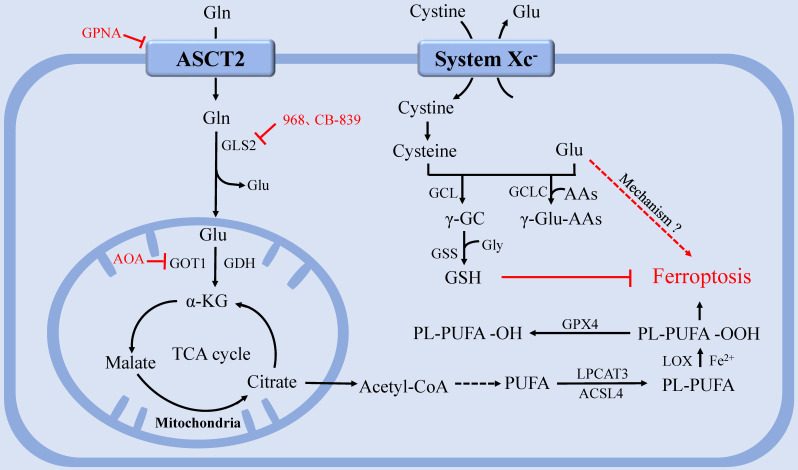
Figure 2.
The regulation of glutamine metabolism in ferroptosis. After entering the cell via the ASCT2, Gln can be degraded and provide a precursor for TCA and PUFAs biosynthesis. System Xc- inputs cysteine to synthesize GSH and exchange Glu at the same time. GPX4 utilizes GSH to eliminate lipid peroxides that participate in ferroptosis. GCLC maintains the Glu pool homeostasis under cystine starvation by mediating the synthesis of γ-glutamine peptide, thereby limiting the accumulation of Glu and protecting against ferroptosis. Abbreviations: ASCT2: solute carrier family 1A5 transporter; Gln: Glutamine; Glu: glutamate; GLS: glutaminase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOT1: aspartate aminotransferase 1; TCA: tricarboxylic acid; PUFAs: polyunsaturated fatty acids; system Xc-: Cystine-glutamate antiporter transport system; GSH: glutathione; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4; GCLC: glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit.