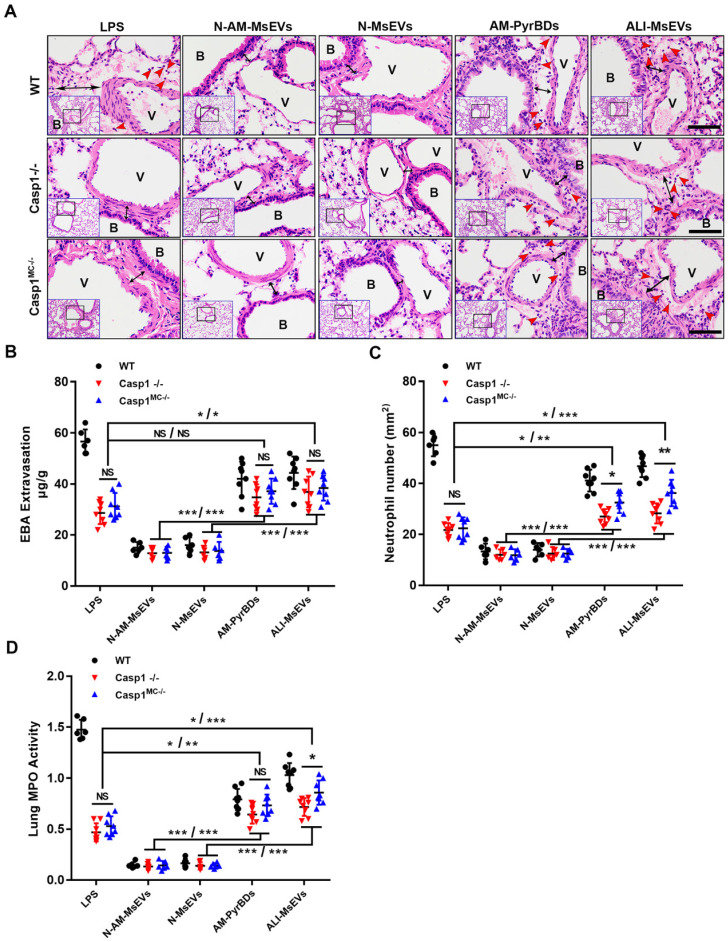
Figure 6.
PyrBDs induce vascular leakage and recruit neutrophils. (A) H&E-stained cross-section of the lung from LPS-exposed or PyrBDs treated WT, Casp1-/-, and Casp1MC-/- mice at 4 h showed that PyrBDs were able to cause extensive neutrophils infiltration of the lung interstitium. The red arrow points to neutrophils; the black arrow indicates interstitial edema; Bar = 50 μm. B, trachea; V, blood vessel. Quantitative analysis of (B) lung vascular leakage (EBA extravasation), (C) neutrophil infiltration, and (D) lung tissue MPO activity. Compared with the N-MsEV and N-AM-MsEV groups, the PyrBD groups showed more severe vascular leakage and neutrophil infiltration. In addition, PyrBDs reversed the resistance of caspase-1 deficiency to LPS to a certain extent. N-AM-MsEVs, normal alveolar macrophages MsEVs; N-MsEVs, normal mouse MsEVs; AM-PyrBDs, pyroptotic alveolar macrophages MsEVs; ALI-MsEVs, ALI-1h mice MsEVs. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, NS, no significant difference; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.