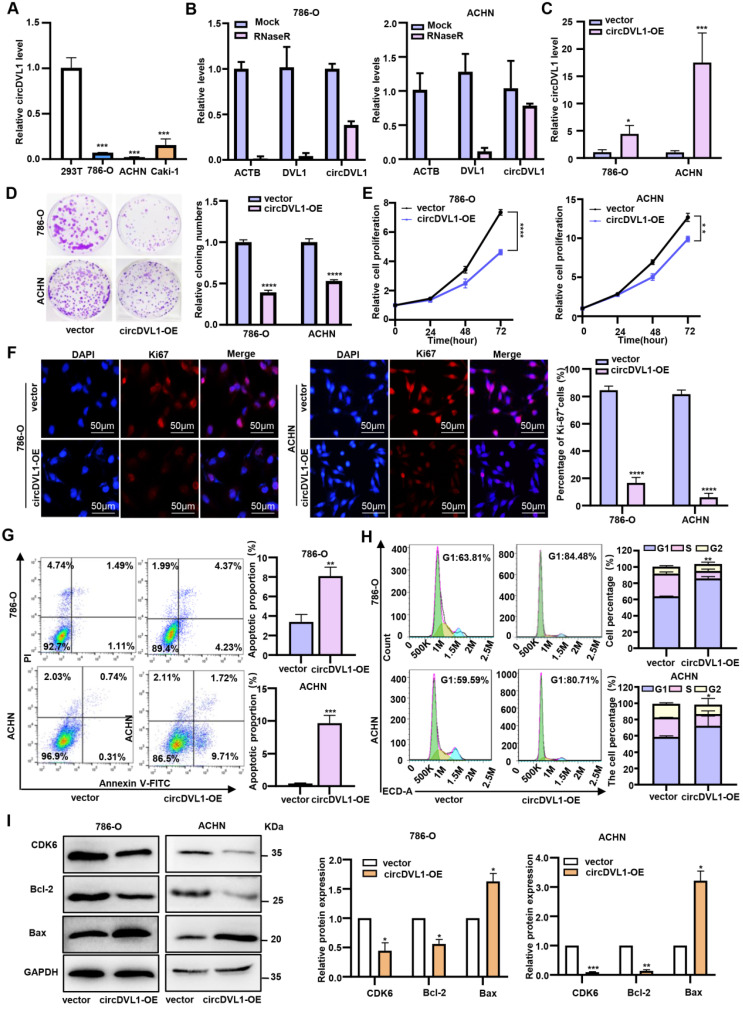
Figure 2.
CircDVL1 inhibits ccRCC cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in vitro. (A) The expression of circDVL1 in several ccRCC cell lines and 293T cells were detected by RT-qPCR. (B) CircDVL1 was tolerant to RNase R. Linear RNAs β-actin (ACTB) and DVL1 were significantly decreased with RNase R, while circDVL1 was almost unaffected. Mock, absence of RNase R. (C) The abundance of circDVL1 in 786-O and ACHN cells transfected with circDVL1 and control vectors (Vector) was determined by RT-qPCR. (D) Colony formation of 786-O and ACHN transfected with circDVL1 overexpression (circDVL1-OE) or control vectors. (E) The proliferation ability of 786-O and ACHN transfected with circDVL1 overexpression or control vectors was assessed with the CCK-8 assay. (F) Ki67 expression of 786-O and ACHN transfected with circDVL1 overexpression or control vectors was assessed with immunofluorescence staining assays. Scale bars: 50 µm. (G) The percentage of apoptosis distributions cells in each stage was evaluated by flow cytometry. (H) Cell cycle profile of 786-O and ACHN transfected with circDVL1 overexpression or control vectors and quantitative analysis of results from two independent experiments are shown. (I) Western blot results of CDK6, Bcl-2, and Bax levels in 786-O and ACHN transfected with circDVL1 overexpression or control vectors, and quantitative analysis of results from two independent experiments are shown. GAPDH expression was served as a loading control. Data are exhibited as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001, no significant (NS).