Figure 5.
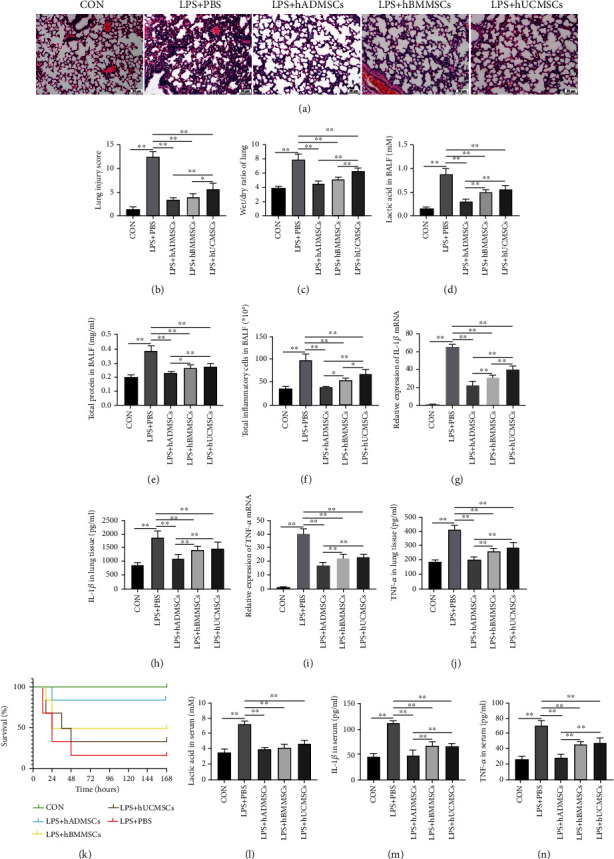
Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) alleviated sepsis-induced ALI and systemic inflammation and improved survival in mice. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of lung tissue sections from the different experimental groups. (b) Lung injury score analysis. (c) Wet-to-dry ratio of lung tissues. (d) Lactic acid content in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). (e) Protein concentration in BALF. (f) Inflammatory cell counts in BALF. mRNA expression of (g) interleukin- (IL-) 1β and (i) tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-) α in lung tissue. Levels of (h) IL-1β and (j) TNF-α in lung tissue measured by ELISA. (k) Survival of mice (n = 12 mice in each group); p < 0.001 among the curves as determined using the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Levels of (l) lactic acid, (m) IL-1β, and (n) TNF-α in serum, as measured by ELISA. Data in (b–j) and (l–n) are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6 in each group); p values were calculated using one-way ANOVA. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01.
