Figure 2.
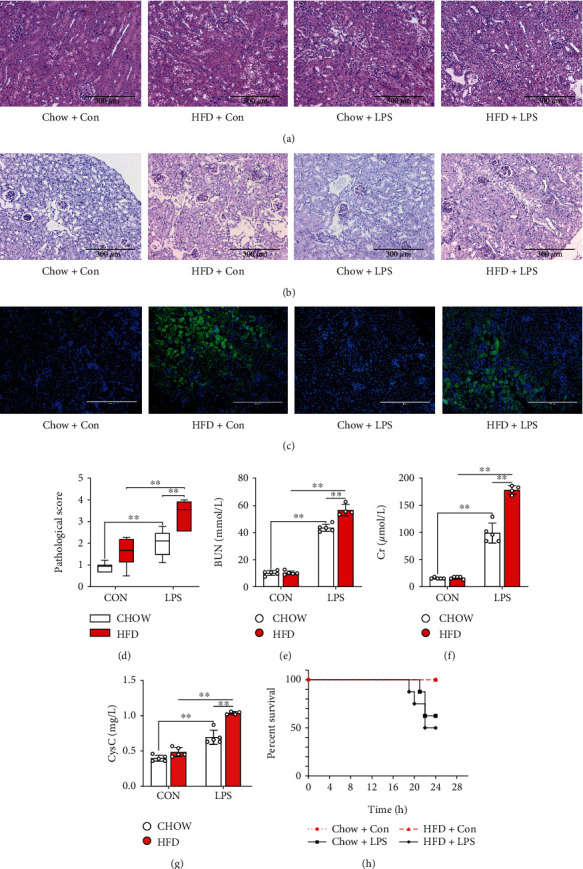
Diabetes-aggravated septic renal injury in mice. Renal pathology was clearly observed via renal H&E ((a) 200x) and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining ((b) 200x). BODIPY staining ((c) 200x) was used to analyze the phospholipid accumulation in the proximal tubular cells of different groups of mice. The pathological score (d) was evaluated according to renal H&E staining. Serum urea nitrogen (BUN) (e), creatinine (CCr) (f), and cystatin C (Cysc) (g) levels, which reflect renal function, were determined. Furthermore, the survival rate (h) of diabetic mice subjected to LPS was calculated. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM (n = 4 − 8). ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's test.
