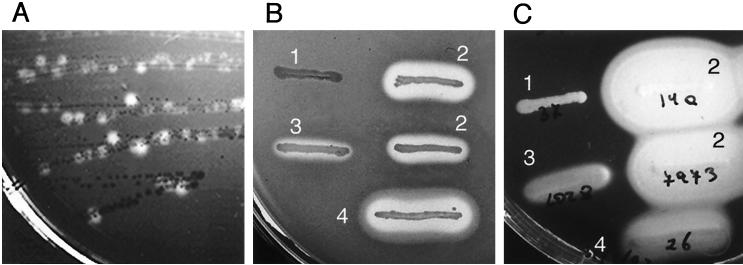
FIG. 12.
Hemolysin (Hly) and lecithinase (PlcB) phenotypes of L. monocytogenes. (A and B) Sheep blood agar; (C) egg yolk agar. (A) Original plate from which prfA* mutants of L. monocytogenes were first isolated and identified; the culture shows a mixture of colonies of the wild-type isolate P14 (weakly hemolytic) and its spontaneous prfA* derivative, P14-A (strongly hemolytic) (see text and references 544 and 545 for details). (B and C) Hly and PlcB phenotypes of L. monocytogenes (streaks 1, 2, and 3) compared with those of L. ivanovii (streak 4). 1, weak to undetectable hemolytic and lecithinase activities typical of the L. monocytogenes wild type (clinical strain P37); 2, strong hemolytic and lecithinase activities of prfA* mutant (strains P14-A and NCTC 7973); 3, intermediate variant phenotype found in strain L028, of unknown molecular basis (L028 has a wild-type prfA); 4, strong hemolytic and lecithinase activities by L. ivanovii (clinical isolate P26); all the strains of this species characteristically overexpress PrfA-dependent virulence genes to levels similar to those of prfA* mutants of L. monocytogenes.