FIG. 6.
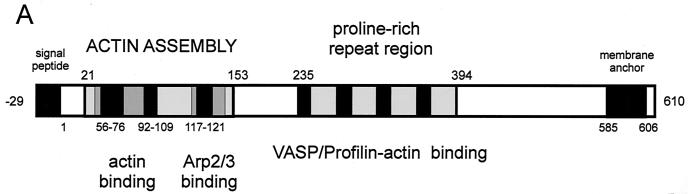
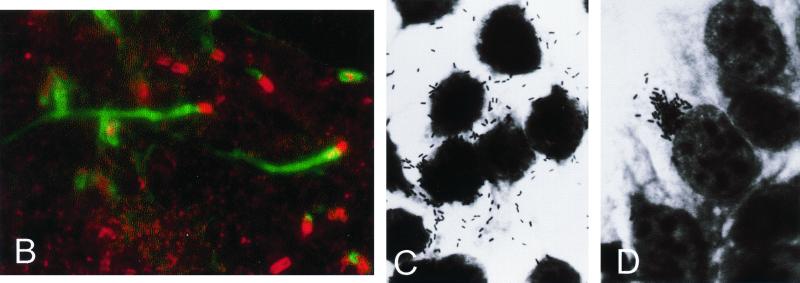
Actin-based intracellular motility. (A) Schematic structure and functional motifs of ActA (see text for details; amino acids numbered according to references 339 and 672). (B) Cos-1 cells infected with L. monocytogenes and labeled with FITC-phalloidin (actin stain, green) and rhodamine-conjugated anti-Listeria antibody (red) at 4 h postinfection; moving bacteria with actin tails are visible. (C and D) Giemsa stain of Caco-2 cells infected with L. monocytogenes wild-type (C) and ΔactA mutant (D) at 4 h postinfection; ΔactA mutant bacteria do not move intracellularly and do not spread to neighboring cells, growing in the cytoplasm as a microcolony close to the nucleus.