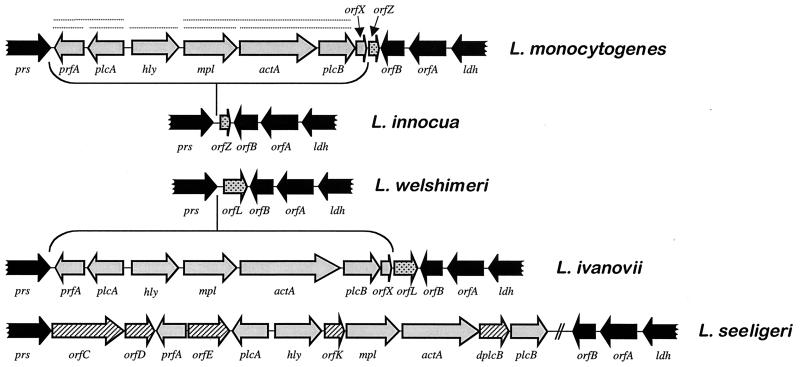
FIG. 8.
Physical and transcriptional organization of the central virulence gene cluster (LIPI-1) of L. monocytogenes and structure of the locus in other Listeria spp. Genes belonging to LIPI-1 are in grey, and the flanking loci are in black. Dotted lines above L. monocytogenes LIPI-1 genes indicate known transcripts. LIPI-1 is inserted in a chromosomal region delimited by the prs and ldh genes, encoding the housekeeping enzymes phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate synthase and lactate dehydrogenase, respectively. In the plcB-ldh intergenic region, two ORFs, orfA and orfB, are found in all Listeria spp., indicating that the insertion point of LIPI-1 is between the prs and orfB loci. In the plcB-orfB intergenic region of L. monocytogenes, there are two small ORFs, orfX and orfZ (stippled), which delimit the putative excision point of LIPI-1 in L. innocua. In the plcB-orfB intergenic region of L. ivanovii, two small ORFs, orfX (encoding a homolog of the orfX product from L. monocytogenes) and orfL (stippled), are also present, which, like those in L. monocytogenes, delimit the deletion point of LIPI-1 in the nonpathogenic species L. welshimeri. orfZ and orfL encode polypeptides with significant similarity to bacteriophage proteins (respectively Orf6 of the A511 Listeria phage and a serine/threonine protein phosphatase from λ [88a, 670a]), suggesting that LIPI-1 was originally acquired by phage transduction (see text for details). The additional ORFs found in the L. seeligeri virulence gene cluster are hatched (the orfK product shows 39% similarity with the phosphatidylinositol phospholipase PlcA and dplcB is a truncated duplicate of the plcB gene). The figure has been constructed using data from references 88a, 232, 350, and 672 and unpublished results from J.K. (L. seeligeri) and B.G.-Z. and J.-A.V.-B. (L. ivanovii). (Adapted from reference 670a with permission of the publisher.)