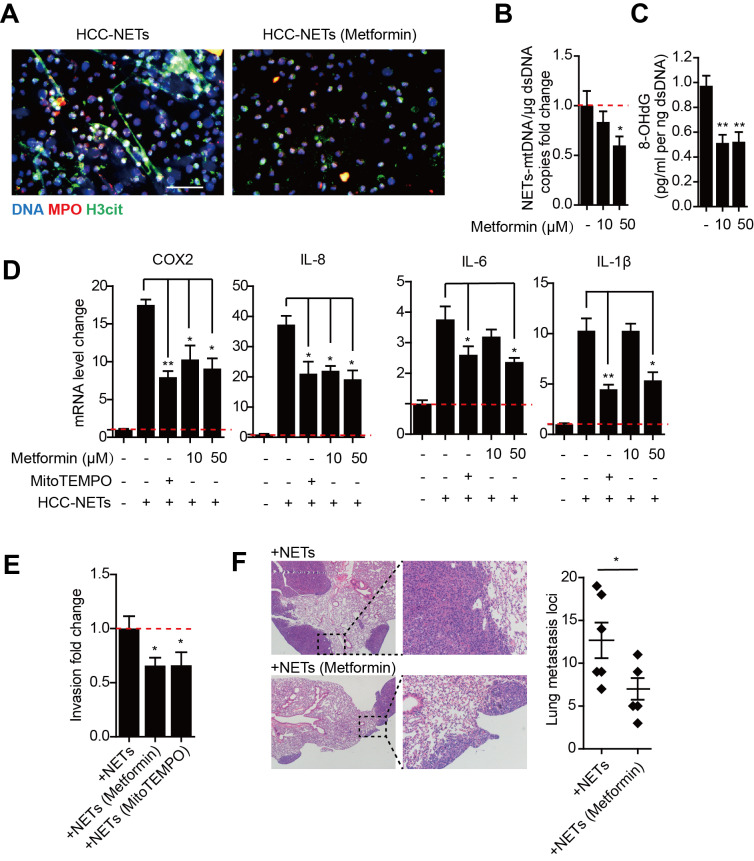
Figure 5.
Diminishing altered oxidized mtDNA-enriched HCC-NETs by metformin reduced tumorous inflammatory response and HCC metastasis. (A) Metformin inhibited HCC-NETs formation. HCC-N were pretreated with or without metformin and stimulated by PMA for 4 hours. NETs were then fixed and stained for DNA, MPO and H3cit, and representative immunofluorescence images were shown. Scare bar: 100μm. (B-C) metformin attuned mtDNA level in NETs (B) and level of 8-OHdG in NETs (C). Data were presented as fold change relative to basal level of each group. (D) Metformin attuned the pro-inflammatory mediators up-regulation in HepG2 cells triggered by HCC-NETs. MitoTEMPO served as a positive control for oxidation inhibition. (E) Metformin inhibited the enhanced invasion capacity induced by HCC-NETs. (F) Metformin abrogated the experimental metastasis in a mice model. Representative of gross lung metastasis and quantification were shown. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01.