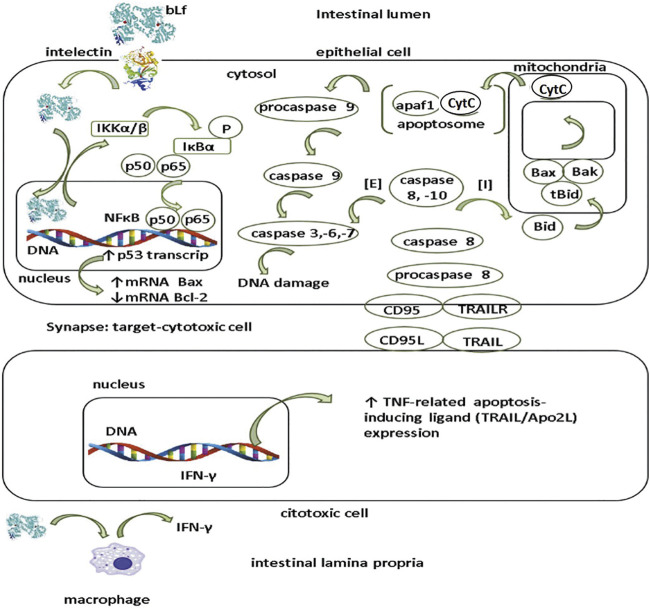
FIGURE 3.
Presumable mechanism of apoptosis by lactoferrin in intestinal tumor cells. Apoptosis pathway may be elicited by lactoferrin (Lf) after being internalized by intelectin (INTL) receptor expressed by intestinal epithelial cells. After translocation, Lf is targeted to nucleus where functions as trans-activator of p53 promotor via NFκB promotor activation. Lf induces the IKKα/β activation and concomitant phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα resulting in the release of NFκB (p50/p65) to nucleus. Activation of p53 gene induces the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax,Bak) while decreases the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins (Bcl-2). Extrinsic (E) apoptosis pathway relies on the ligation of surface molecules on target cells CD95 (Fas/Apo1) and/or TRAILR with their corresponding ligands on the cytotoxic cells CD95L and/or TRAIL respectively. Interaction ligand-receptor enables the conversion of inactive procaspase 8 in the active form as caspase 8. Caspase 8 forms a complex with caspase 10 that triggers sequentially the cascade of activation of caspase -3,-6 and -7 resulting in DNA fragmentation. Intrinsic (I) pathway collaborates in the apoptosis of tumor cells. In this route, caspase 8 and -10 split Bid into the active form tBid (truncated Bid) which in turn activates Bax and Bak. Both Bax and Bak facilitate the outcome of cytochrome C (cytC) from the mitochondrial intermembrane space to the cytosol. Once translocated to cytosol, cytC together with apaf1, form a protein complex called as apoptosome that activates procaspase 9 into caspase 9 that in turn elicits the activation of caspase -3, -6 and -7 resulting in DNA damage. Additionally, at subepithelial level (lamina propria), Lf may enhance apoptosis of tumor cells by eliciting the IFN-γ in macrophages that upmodulates the expression of TRAIL in cytotoxic cells.