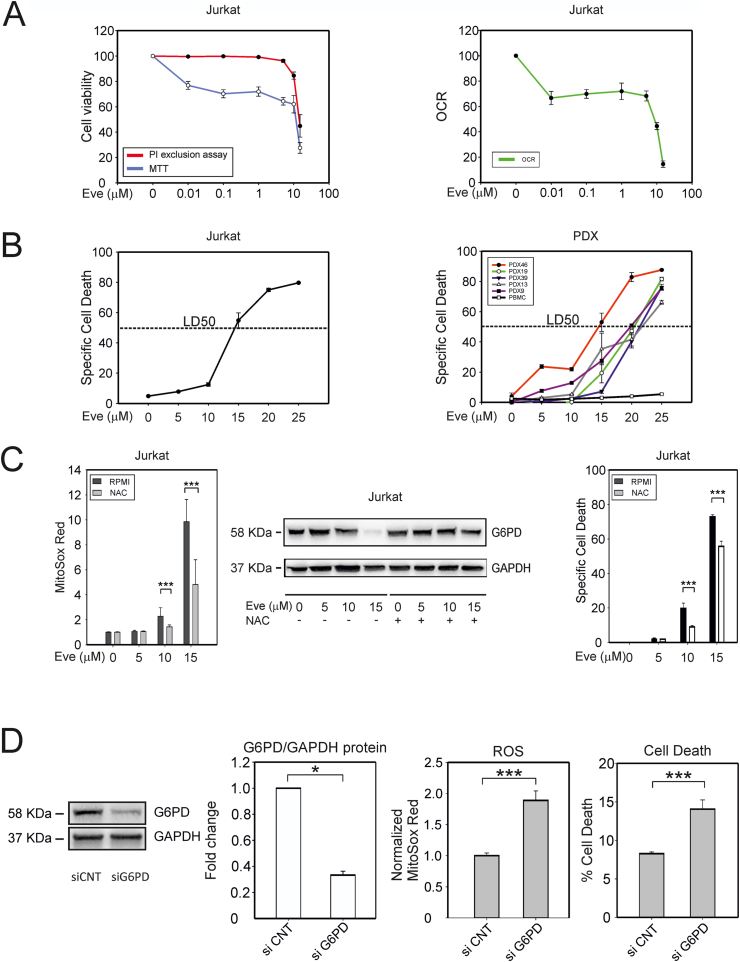
Fig. 4.
Dose-dependent effects of everolimus on T-ALL cell viability. (A) Effects of 24 h' treatment with everolimus on Jurkat cell viability and oxygen consumption rate. The left-hand graph shows cell viability assessed with the MTT assay (which measures NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductases; blue line), and the PI exclusion test, which tests plasma membrane integrity (red line). The right-hand graph shows the basal oxygen consumption rate (OCR, a proxy of mitochondrial OXPHOS activity) measured with a Seahorse XF Analyzer. (B) Quantitative evaluation of cell death in response to 24 h' treatment with different doses of everolimus revealed a lethal dose 50 (LD50) of approximately 15 μM in Jurkat (left) and PDX (right) cells. (C) Effects of the ROS scavenger NAC in everolimus-treated Jurkat cells. NAC (500 μM) was added to the cultures 16 h before addition of the indicated concentrations of everolimus; cells were analyzed 24 h later. The left-hand graph shows ROS measured with MitoSOX Red and flow cytometry. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) data were normalized against the MFI of the control. Shown are mean values and standard error bars from 3 independent experiments, 3 replicates each. The middle panel shows representative immunoblots to detect G6PD and GAPDH proteins. The right-hand graph shows specific cell death detected by PI staining and flow cytometry (3 independent experiments, 3 replicates each). (D) Jurkat cells were electroporated with siRNA against G6PD or with control siRNA, cultured for 24 h, and analyzed for the expression levels of G6PD protein, ROS accumulation using MitoSox Red, and cell death measured as percentages of PI-positive cells.
The indicated pairwise comparisons were statistically significant with the Mann-Whitney test (*** indicates p values < 0.001 and * < 0.05). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)