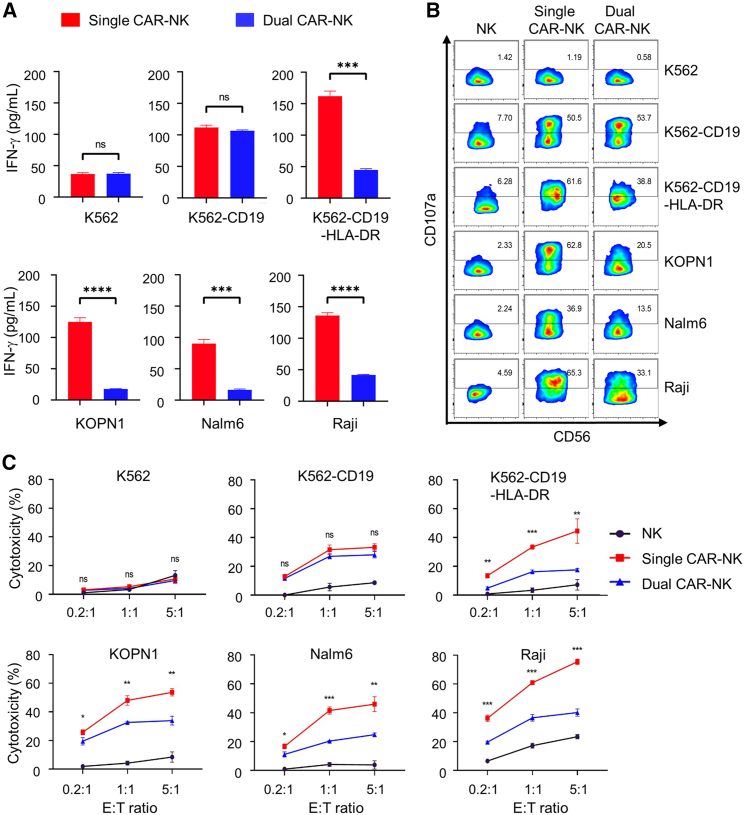
Figure 4.
Dual CAR-NK cells preferentially recognize and kill HLA-DRneg cells over HLA-DR+ cells in vitro
(A) Comparison of IFN-γ production by single and dual CAR-NK cells in response to different target cells. Single and dual CAR-NK cells were incubated with each of the six target cells (K562, K562-CD19, K562-CD19-HLA-DR, KOPN1, Nalm6, and Raji) at an E:T ratio of 1:1 for 4 h at 37°C. The cell culture supernatant was collected, and the concentration of IFN-γ was measured by ELISA. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of triplicates. (B) Comparison of CD107a expression by single and dual CAR-NK cells in response to different target cells. Single and dual CAR-NK cells were incubated with each of the six target cells for 1 h at 37°C, in the presence of a PE-conjugated anti-CD107a antibody. Cells were then treated with monensin (GolgiStop), incubated for 4 h, stained with an anti-CD56 antibody, and analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentage of CD107a+ cells was determined, which indicates the level of degranulation. Unmodified NK-92MI cells were used as a negative control. (C) Comparison of the cytotoxicity of single and dual CAR-NK cells against different target cells. The percentage of cytotoxicity was measured by LDH release. Unmodified NK-92MI cells were used as the negative control. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical significance is calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05; n.s., not significant.