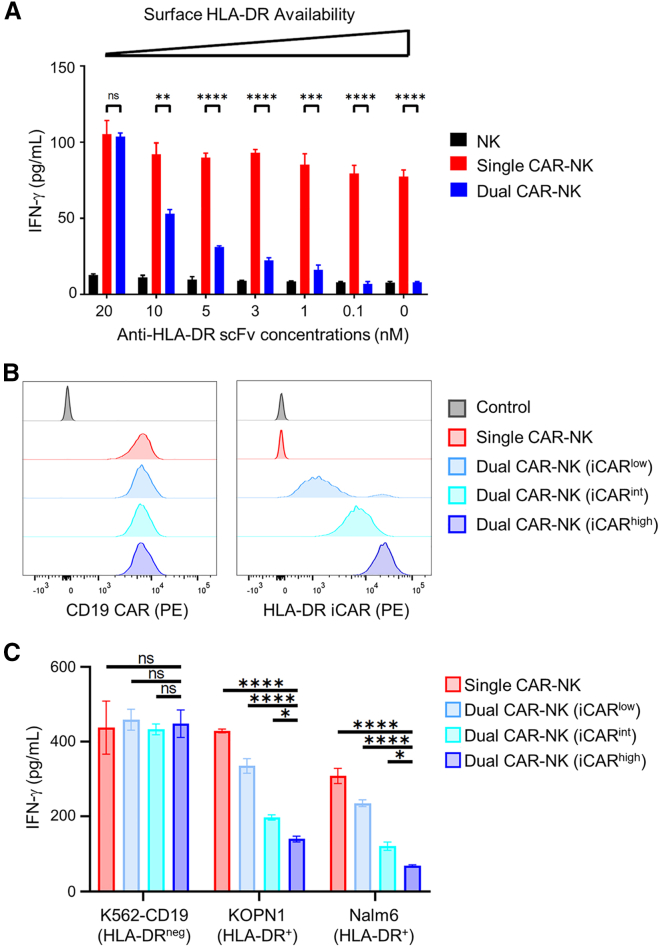
Figure 5.
The level of iCAR-mediated inhibition is dependent on the availability of HLA-DR on target cells and iCAR on effector cells
(A) The HLA-DR antigens on K562-CD19-HLA-DR cells were blocked with different concentrations of anti-HLA-DR scFv. These cells were then cocultured with NK, single CAR-NK, and dual CAR-NK cells, respectively. After 4 h, the IFN-γ level in the coculture supernatant was assessed by ELISA. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of two independent experiments. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of single CAR-NK cells and three dual CAR-NK cell populations expressing HLA-DR iCAR at different levels. Cells were stained with a PE-labeled anti-FMC63 scFv antibody (for CD19 CAR) and a PE-labeled anti-FLAG tag antibody (for HLA-DR iCAR) at saturating concentrations, respectively. Untransduced NK-92MI cells were used as the negative control. (C) Comparison of IFN-γ production by single and the three dual CAR-NK cells against K562-CD19, KOPN1, or Nalm6 cells. Cells were incubated at a 1:1 E:T ratio for 4 h. The concentrations of IFN-γ were measured by ELISA. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of two independent experiments. Statistical significance is calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05; n.s., not significant.