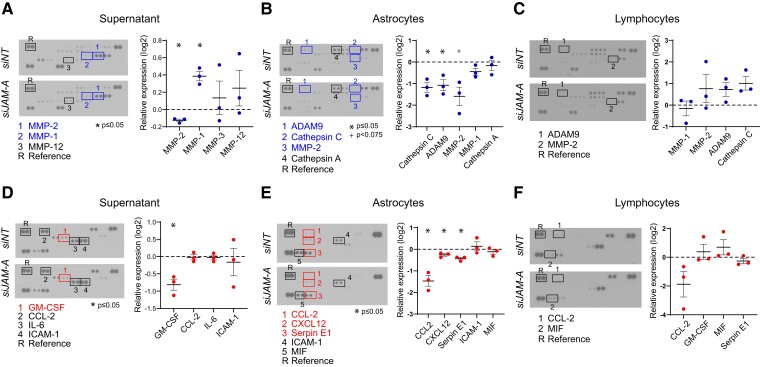
Figure 3.
Astrocytic JAM-A increases pro-inflammatory protease and cytokine levels in astrocyte-CD3+ T-cell co-culture. Astrocytes were transfected with JAM-A or non-targeted siRNA (siJAM-A versus siNT), then co-cultured with CD3+ T cells for 24 h and samples processed for human protease and cytokine ELISA immunoassays. (A–C) JAM-A knock-down in astrocytes led to an increase of MMP-1 (relative log2 expression 0.38, P = 0.019) and a decrease of MMP-2 (relative log2 expression −0.13, P = 0.014) in the supernatant and decrease of ADAM9 (relative log2 expression −1.074, P = 0.05) and cathepsin C (relative log2 expression −1.174, P = 0.006) in astrocyte lysates (B). There were no significant changes in protease levels seen in lymphocyte lysates (C). (D–F) Astrocytic JAM-A knock-down led to decreased levels of (D) GM-CSF (relative log2 expression −0.79, P = 0.04) in the supernatant and (E) CCL-2 (relative log2 expression −1.3, P = 0.03), CXCL12 (relative log2 expression −0.13, P = 0.04) and serpin E1 (relative log2 expression −0.3, P = 0.03) in astrocytic lysates. There were no significant changes in cytokine levels seen in lymphocyte lysates (F). Data (A–F) are from three biological replicates; two-tailed paired t-tests were performed on probes demonstrating a visually detectable signal in normalized expression values relative to a reference control.