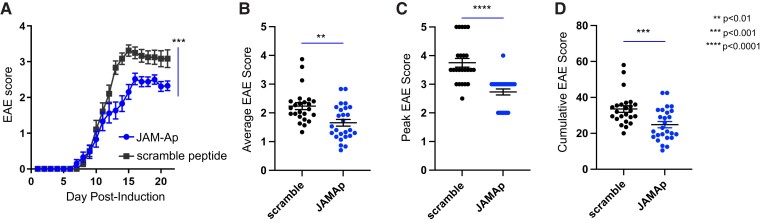
Figure 6.
Treatment with a JAM-Ap reduced clinical disease severity during EAE. (A) WT mice with EAE treated with daily intraperitoneal injection of a JAM-Ap from Day 7 post-immunization showed a significantly milder course of clinical disability compared with scramble peptide-treated controls. Differences in the disease progression over time were assessed with the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test (P = 0.0005). Average (B), peak (C) and cumulative (D) scores of the EAE trial shown in (A) were significantly lower in JAM-Ap-treated mice compared with scramble peptide-treated mice [average score: 2.23 (scramble) versus 1.65 (JAM-Ap), P = 0.001; peak score: 3.75 (scramble) versus 2.73 (JAM-Ap), P < 0.0001; cumulative score: 33.54 (WT) versus 24.83 (CKO), P = 0.001, Mann–Whitney tests]. Average in graphs shown with SEM. Graphs (A–D) show pooled data from three independent EAE experiments with a minimum of eight mice per group for each experiment, total JAM-Ap n = 24, scramble n = 26.