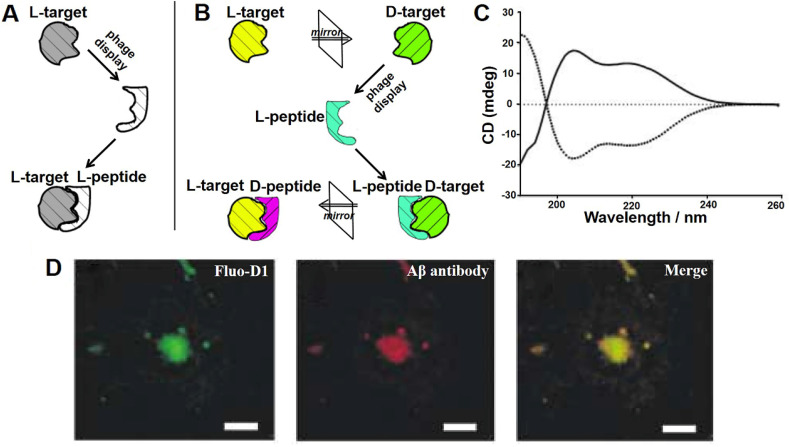
Figure 4.
Mirror image phage display and its application in AD. Schematic representation of the principles of (A) common phage display and (B) mirror-image phage display. (A) A phage displayed peptide library is screened for L-peptide that bind to a given target, which consists of L-amino acids (L-target). (B) A phage displayed peptide library is screened for L-peptide that bind to a given target, which consists of D-amino acids (D-target). The peptide composed of D-amino acids (D-peptides) with the same L-peptide sequence could bind to naturally occurring L-target. (C) CD analysis showed that biotin-L-Aβ (1-42) (dotted line) and biotin-D-Aβ-(1-42) (solid line) had mirror symmetry. The Aβ composed of all-D amino acid residues was prepared as the target for phage selection. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of brain sections of AD patient with fluorescently labeled D1 (Fluo-D1) and commercially Aβ antibody with a Cy3-labeled secondary antibody. Reprinted with permission from 40, 43. Copyright 2003 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.