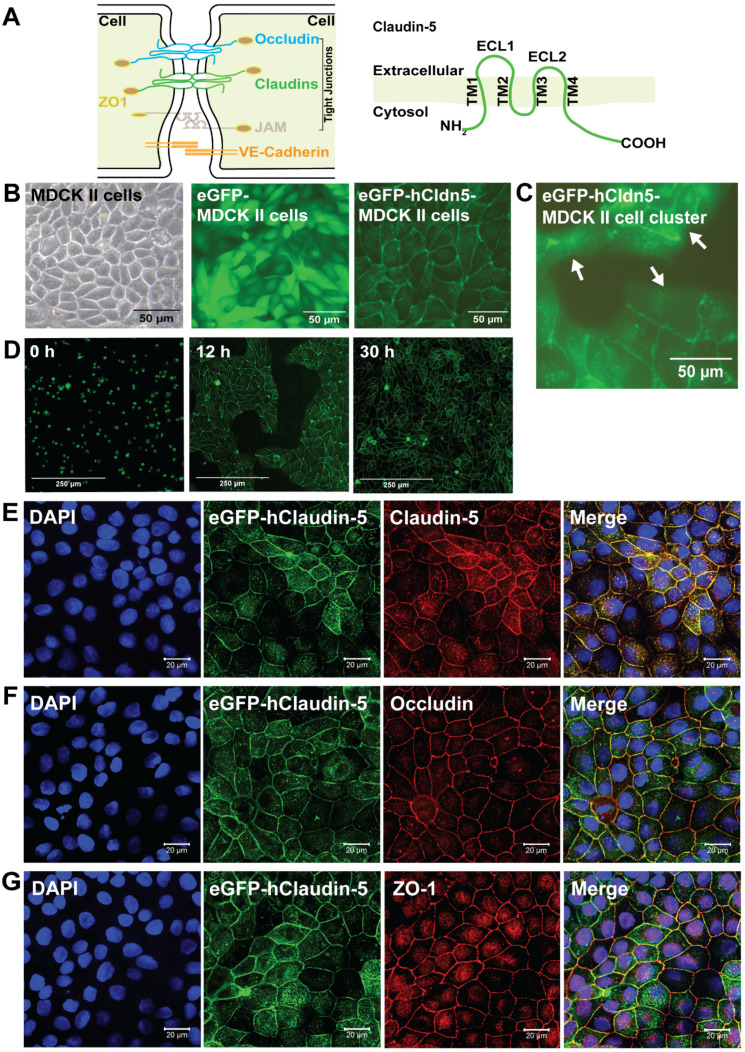
Figure 1.
eGFP-hCldn5-MDCK II cells exhibit a tight monolayer and human claudin-5 is localized to cell/cell contacts. (A) Scheme of tight junctions formed by proteins such as claudin-5, occludin, and ZO-1. Domain structure of claudin-5. (B) Representative phase contrast image of confluent parental MDCK II cells and epifluorescence images of confluent MDCK II cells expressing eGFP only (eGFP-MDCK II) or eGFP-tagged human claudin-5 (eGFP-hCldn5-MDCK II). (C) Epifluorescence images of isolated clusters of eGFP-hCldn5-MDCK II cells. White arrows indicate the absence of localization of eGFP fluorescence in areas without cell/cell contacts. (D) Time-lapse fluorescence images of eGFP-hCldn5-MDCK II cells from the time of seeding at a density of 200,000 cells/cm2 (0 h) to complete formation of a confluent monolayer (30 h). (E) Expression of claudin-5, (F) occludin and (G) ZO-1, localized to cell/cell borders. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars: 50 µm (B-C), 250 µm (D) and 20 µm (E-G).