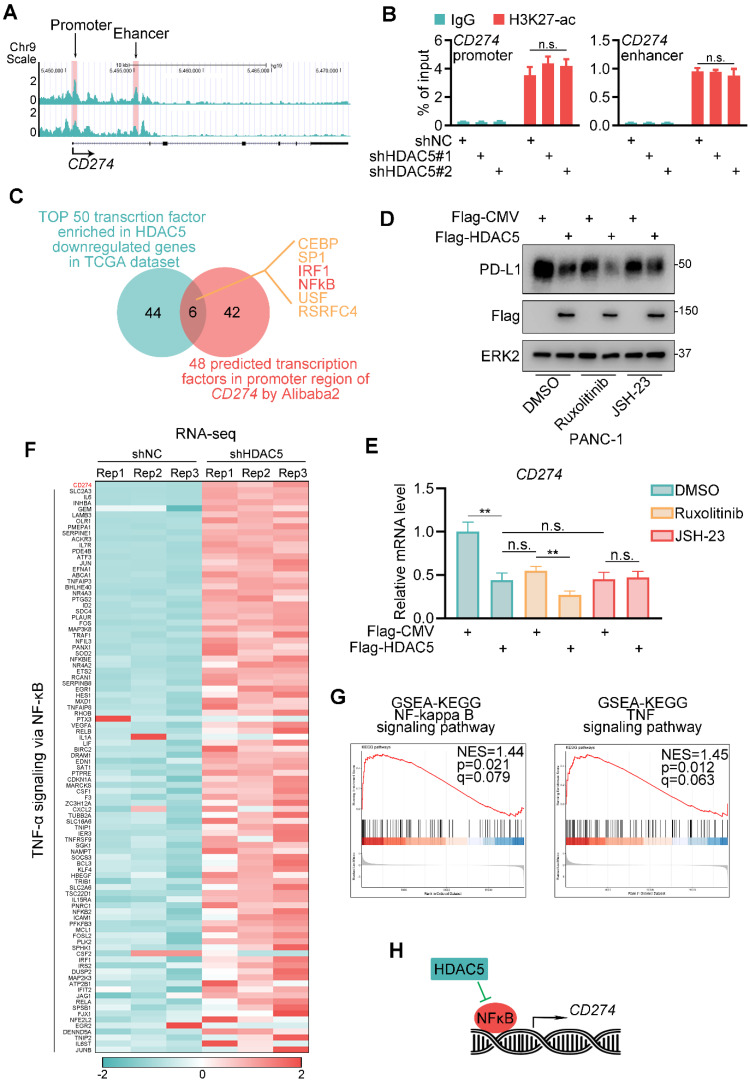
Figure 2.
HDAC5 modulates NF-κB dependent expression of PD-L1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser screen shot of H3K27-ac ChIP-seq tracks at the gene loci of CD274. (B) PANC-1 cells were infected with lenti-virus expressing indicated shRNAs for 48 h. After 48 h puromycin selection, cells were harvested for ChIP-qPCR analysis to detect the H3K27-ac enrichment at promoter or enhancer region of CD274. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3, n.s. not significant). (C) Venn diagram depicting the predicted HDAC5 regulated transcription factor of CD274. (D-E) PANC-1 cells were transfected with indicated plasmid. 24 h after transfection, cells were treated with indicated drugs for 24 h (2.5 µM Ruxolitinib, 10 µM JSH-23). Then cells were harvested for western blot analysis (D) and RT-qPCR. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3, n.s. not significant, ** P < 0.01) (E). (F) Heatmap showing the expression of CD274 and a subset of genes involved in TNF-α-NF-κB pathway. (G) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of the indicated pathways. (H) Model depicting the mechanism that HDAC5 regulates PD-L1 expression in an NF-κB dependent manner.