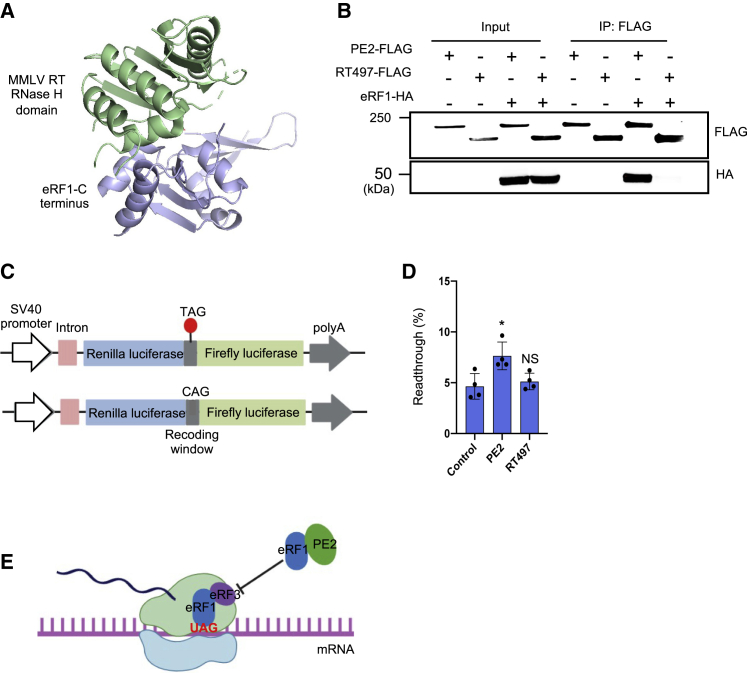
Figure 5.
PE2 increases stop codon readthrough through the RNase H domain
(A) Structure of the M-MLV RNase H domain/eRF1 complex (PDB: 5DMQ). (B) CoIP of PE2 with eRF1. Plasmid constructs of PE2-FLAG or RT497-FLAG were co-transfected with eRF1-HA into HEK293T cells. Empty vectors expressing each tag (FLAG, HA) were used as negative controls. (C) Schematic of the dual luciferase bicistronic vector used in translational readthrough assays. The red dot represents the stop codon. (D) PE2 but not RT497 overexpression promotes stop codon readthrough. PE2, RT497, or control vector were co-transfected with dual luciferase reporter in HEK293T cells. The ratio of Firefly:Renilla from each experimental group was normalized to a control reporter lacking a stop codon between Firefly and Renilla. (E) Model of PE2 promoting stop codon readthrough. PE2 interacts with eRF1 via the RNase H domain, which inhibits the binding of eRF1 with eRF3, promoting stop codon readthrough.