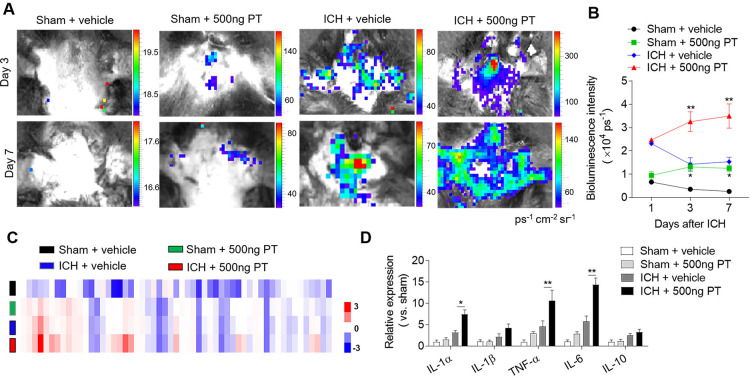
Figure 2.
Pertussis toxin (PT) enhances brain inflammation after intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH). ICH in mice was induced using 0.0375 U collagenase injection. PT treatment was given immediately after ICH by intraperitoneal injection, at a dose of 500 ng. (A, B) At day 1, day 3 and day 7 after ICH, representative bioluminescence images and quantification analysis show reactive oxygen species generation in sham and ICH mice receiving PT or vehicle. n=3 mice per group from two independent experiments. (C) Brain tissues were obtained from ICH mice receiving PT or vehicle. Sham-operated mice receiving PT or vehicle were used as control. Brain homogenates were analysed by a Mouse XL Cytokines Array kit. Heat map and cluster analysis show the expression of inflammatory factors in brain homogenates from sham and ICH mice with indicated treatments. A heat map was generated and the relative pixel intensity of spots signal is indicated by the representative colour code (red, upregulated; blue, downregulated). (D) Bar graphs show the top significantly dysregulated factors. n=6 mice per group. The data were calculated as mean±SEM; *p<0.05; **p<0.01.