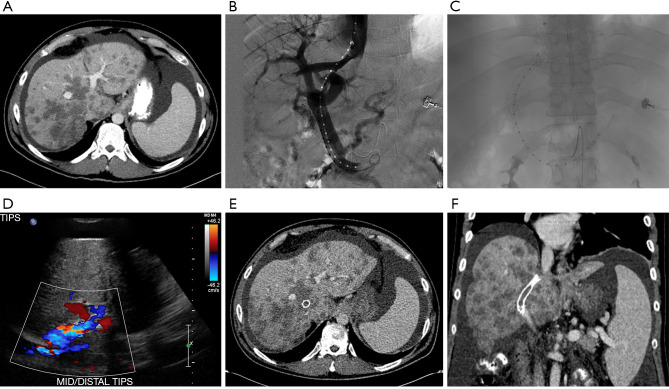
Figure 1.
Patient with colorectal cancer complicated by extensive metastatic disease to the liver. (A) Computerized tomography (CT) is notable for evidence of radiologic pseudocirrhosis including multifocal capsular retraction, segmental volume loss and caudate hypertrophy, as well as diffuse ascites; (B,C) transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement; (D) post-TIPS ultrasound with color doppler showing appropriate flow through the TIPS stent; (E) post-TIPS axial CT image notable for appropriate placement of the stent extending through the liver and multiple hepatic metastases; (F) post-TIPS coronal CT image notable for appropriate placement of the stent extending through the liver and multiple hepatic metastases.