Figure 4. OTULIN variants compromise binding of OTULIN to linear ubiquitin and differentially affect OTULIN’s intrinsic stability and catalytic activity.
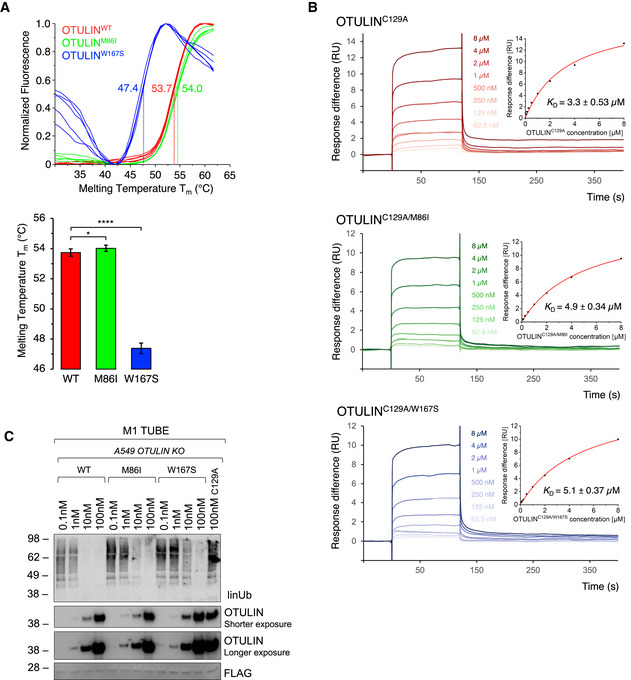
- DSF measurements with OTULINWT, OTULINM86I, or OTULINW167S. Melting temperatures (T m ) are calculated from five independent experiments with standard deviations. *P = 0.011; ****P = 6.64 × 10−18, unpaired t‐test.
- SPR measurements and steady‐state binding curves with calculated dissociation constants (Kd ) after injection of a concentration series of OTULINC129A, OTULINC129A/M86I, or OTULINC129A/W167S to CM5‐immobilized di‐ubiquitin chains.
- Linear ubiquitin linkages isolated from A549 OTULIN KO cells by M1 TUBE assay were incubated with increasing concentrations of recombinant OTULINWT, OTULINM86I, and OTULINW167S or catalytically inactive OTULINC129A as control for 1 h. Afterward, samples were subjected to analysis by Western blot for the indicated proteins. Images are representative of three independent experiments.
