Figure 5. In silico simulation (ISS) model validation and simulated urinary oxalate (UOx) lowering subsequent dietary oxalate removal by SYNB8802.
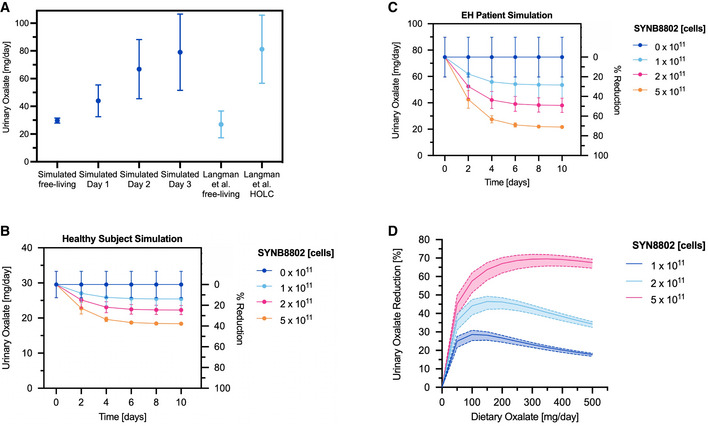
- Validation of simulated UOx excretion against clinical data. Simulated UOx on a free‐living diet and on 3 days of a high‐oxalate diet (dark blue). Observed UOx on a free‐living diet and on 3 days of a high‐oxalate, low‐calcium (HOLC) diet (light blue); points and error bars represent mean and standard deviation, respectively, across 30 simulated healthy subjects.
- Simulated UOx and UOx reduction for healthy subjects consuming 200 mg/day dietary oxalate without SYNB8802 and with 1 × 1011, 2 × 1011, and 5 × 1011 SYNB8802 cells TID over 10 days. Points represent simulations under a baseline assumption of dietary oxalate absorption in healthy subjects (Holmes et al, 2001) (See Materilas and Methods for a detailed description). Error bars represent a simulated range of dietary oxalate absorption (two simulations: 0.75× baseline and 1.25× baseline).
- Simulated UOx and UOx reduction for enteric hyperoxaluria patients consuming 200 mg/day dietary oxalate without SYNB8802 and with 1 × 1011, 2 × 1011, and 5 × 1011 SYNB8802 cells TID over 10 days. Points represent simulations under a baseline assumption of increased dietary oxalate absorption in HOX patients (4× healthy absorption). Error bars represent a simulated range of increased dietary oxalate absorption (two simulations: 3× healthy absorption and 5× healthy absorption).
- Simulated UOx reduction for enteric hyperoxaluria patients after 5 days dosing with 1 × 1011, 2 × 1011, and 5 × 1011 SYNB8802 cells TID as a function of dietary intake of oxalate. Solid curves represent simulations under a baseline assumption of increased dietary oxalate absorption in HOX patients (4× healthy absorption). Shaded regions represent a simulated range of increased dietary oxalate absorption (two simulations: 3× healthy absorption and 5× healthy absorption).
