Figure 2.
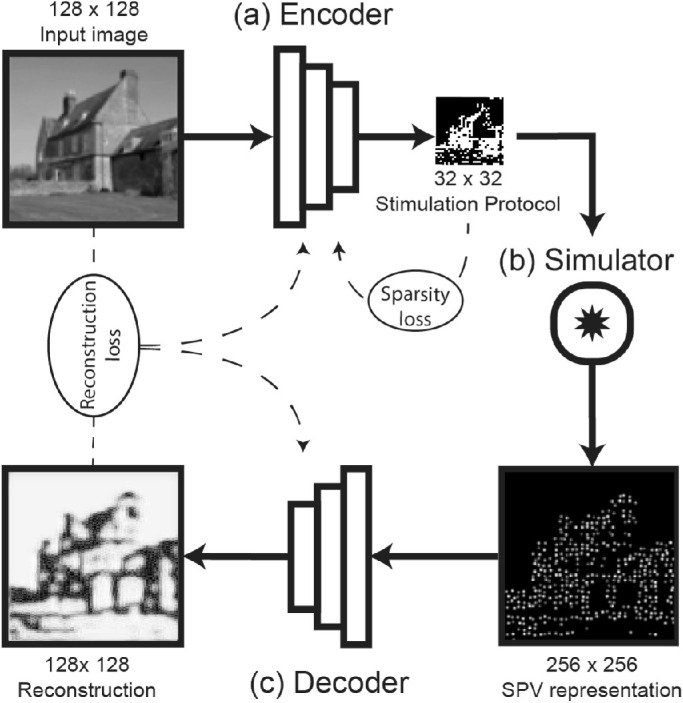
Schematic representation of the end-to-end model and its three components. (a) The phosphene encoder finds a stimulation protocol, given an input image. (b) The personalized phosphene simulator maps the stimulation vector into a simulated phosphene vision (SPV) representation. (c) The phosphene decoder receives a SPV-image as input and generates a reconstruction of the original image. During training, the reconstruction dissimilarity loss between the reconstructed and original image is backpropagated to the encoder and decoder models. Additional loss components, such as sparsity loss on the stimulation protocol, can be implemented to train the network for specific constraints.
