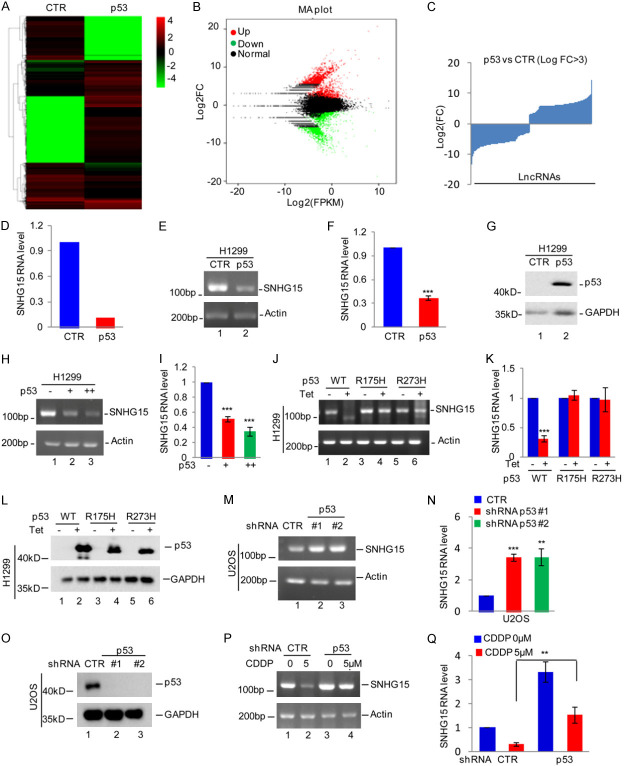
Figure 1.
p53 downregulates SNHG15 expression. (A-C) p53 Tet-on H1299 cells were treated with or without doxycycline for 24 h. Cells were then subjected to RNA sequencing analysis (A), and the differentially expressed genes are shown (B, C). (D) The expression level of SNHG15 was shown. (E-G) The expression of wild-type p53 was induced by doxycycline in H1299 cells, and SNHG15 expression was analyzed using RT-PCR and qRT-PCR (E, F). The expression of p53 was detected using Western blotting (G). (H, I) Wild-type p53 was introduced into H1299 cells, and then SNGH15 expression was analyzed using RT-PCR and qRT-PCR (H, I). (J-L) RT-PCR and qRT-PCR data showing SNHG15 expression in H1299 cells transfected with wild-type p53 or mutant p53 (R175H or R273H) constructs and induced by doxycycline (J, K). Western blot analysis showing the expression of p53 or its mutant protein (L). (M-O) RT-PCR and qRT-PCR data showing SNHG15 expression in U2OS cells with p53 knockdown (M, N). Western blot analysis showing the expression of p53 (O). (P, Q) U2OS cells with or without p53 knockdown were treated with cisplatin (CDDP). SNHG15 expression was analyzed using RT-PCR and qRT-PCR.