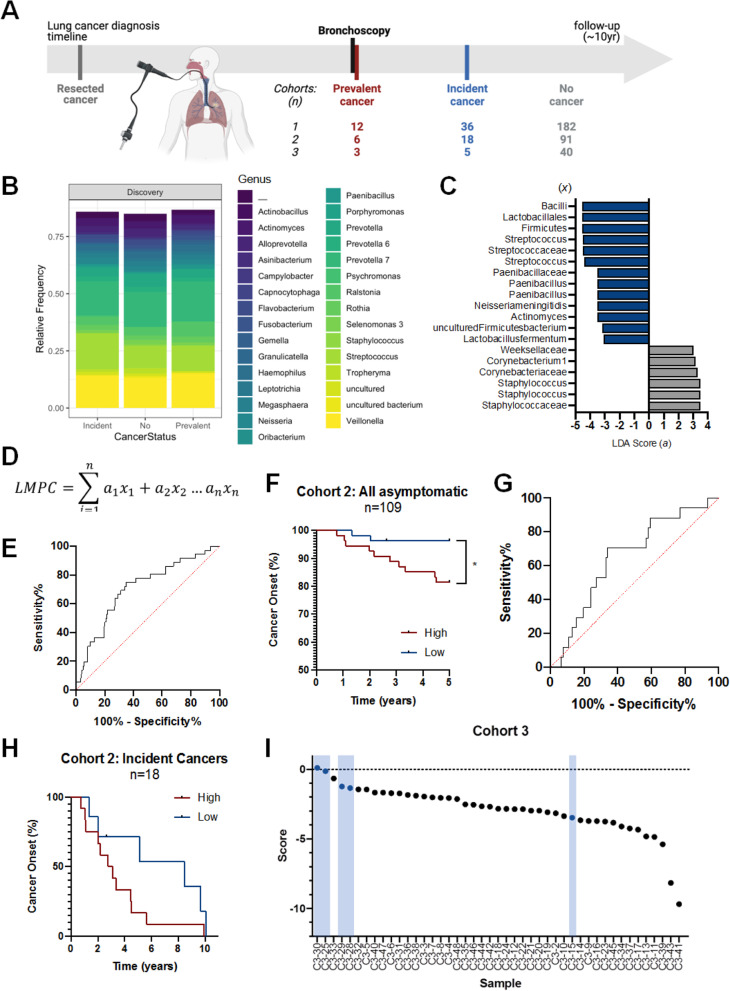
Fig. 1.
Microbiome-based LMPC classifier identifies cancer onset in independent cohort of patients at risk of lung cancer. A Timeline of bronchial sampling in Cohorts 1-3. B Relative abundance of taxa in the microbial communities Cohorts 1 is shown at genus level of classification. C Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) scores of taxonomic features included in the LMPC scoring model. A score magnitude of 4 was used as a cut-off for significant features, with a Kruskal-Wallis p-value of <0.05. Grey bars represent taxa that are higher in relative abundance in No Cancer participants, while blue bars represent taxa with higher relative abundance in Incident Cancer participants. D Formula used to construct LMPC score, where a represents the LDA score value and x represents the relative abundance of each taxa (described in Fig. 1C). E Receiver Operating Characteristic AUC differentiates Incident Cancer participants from No Cancer participants in Cohort 1 (p<0.0001, AUC: 0.7057, 95% CI: 0.6118 to 0.7997). F When the Incident Cancer (n = 18) and No Cancer participants (n = 91) in Cohort 2 were combined and stratified by risk score, those with high scores (red) had significantly earlier cancer diagnosis than those with low score (blue). G Within the Incident Cancer patient group, those with high scores demonstrated shorter time to cancer diagnosis than those with low scores. In both analysis, samples were separated into two groups based on the median score value. H Using a Receiver Operating Characteristic AUC as defined by the score, we are able to differentiate Incident Cancer participants from No Cancer participants in Cohort 2 (p=0.0498, AUC: 0.6503, 95% CI: 0.5167-0.7839). I In an independent cohort (Cohort 3), incident cancer participants comprised 4 of the top 5 largest score values. Incident cancer participants are shown in blue, while participants who did not have a diagnosed cancer with follow-up are indicated in black. Cancer onset was assessed using receiver operating curves and log-rank tests, where p<0.05 was considered significant