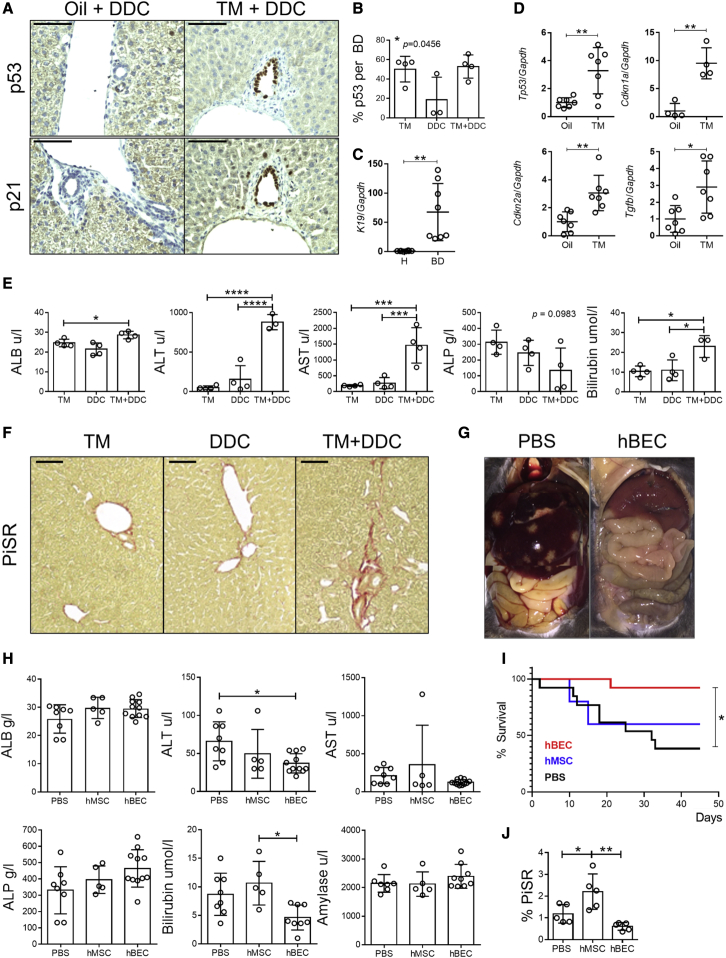
Figure 3.
CD133+ hBECs transplant in an immunodeficient model of biliary disease
(A) Immunostaining for p53 and p21 in control animals (Oil+DDC) versus induced animals (TM+DDC) (n = 3–4). Scale bars, 120 μm.
(B) Quantification of p53-positive cells per bile duct in tamoxifen (TM), DDC diet (DDC) and induced mice (administered with tamoxifen and DDC diet, TM+DDC). ∗ denotes p < 0.05 (mean ± SEM), one-way ANOVA (n = 3–4).
(C) Confirmation of cholangiocyte (K19) gene expression in isolated bile ducts (BDs) and absence in hepatocytes (H) normalized to Gapdh. ∗∗ denotes p < 0.005 (mean ± SEM), Student’s t test (n = 7).
(D) Gene expression analysis of isolated BDs in control (oil) versus induced (TM) mice shows a significant increase in senescent markers in the later population (Trp53, Cdkn1a, Cdkn2a, and Tgfb, normalized to Gapdh). ∗ denotes p < 0.05, ∗∗ denotes p < 0.005 (mean ± SEM), Student’s t test (n = 7).
(E) Transaminase analysis in TM, DDC, and induced mice (TM+DDC). ∗ denotes p < 0.05, ∗∗∗ denotes p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗ denotes p < 0.001 (mean ± SEM), one-way ANOVA (n = 4).
(F) PicroSirius red staining (PiSR) increases in induced mice (TM+DDC), (n = 3). Scale bars, 250 μm.
(G) Representative postmortem image of peritoneum in PBS control and hBEC-transplanted Krt19CreERMdm2fl/flRag2−/−Il2rg−/− mice (n = 4).
(H) Transaminase analysis in PBS control (PBS), human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs), and hBEC-transplanted mice (hBEC). ∗ denotes p < 0.05 (mean ± SEM), one-way ANOVA (n = 5–8).
(I) Survival analysis of mice receiving hBEC (n = 13), PBS (n = 13), or hMSC (n = 5). ∗ denotes p < 0.05 log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test.
(J) PiSR quantification in PBS control (PBS), hMSC-transplanted mice (hMSC), and hBEC-transplanted mice (hBEC) shows a significant reduction of fibrosis. ∗ denotes p < 0.05 (mean ± SEM), one-way ANOVA (n = 5).